Two-stage reproduction derived from cells of thallus could directly contribute to seeds for green tidal algal Enteromorpha(Ulva) prolifera/clathrata bloom, with disclosure of their ephemeral trait
-
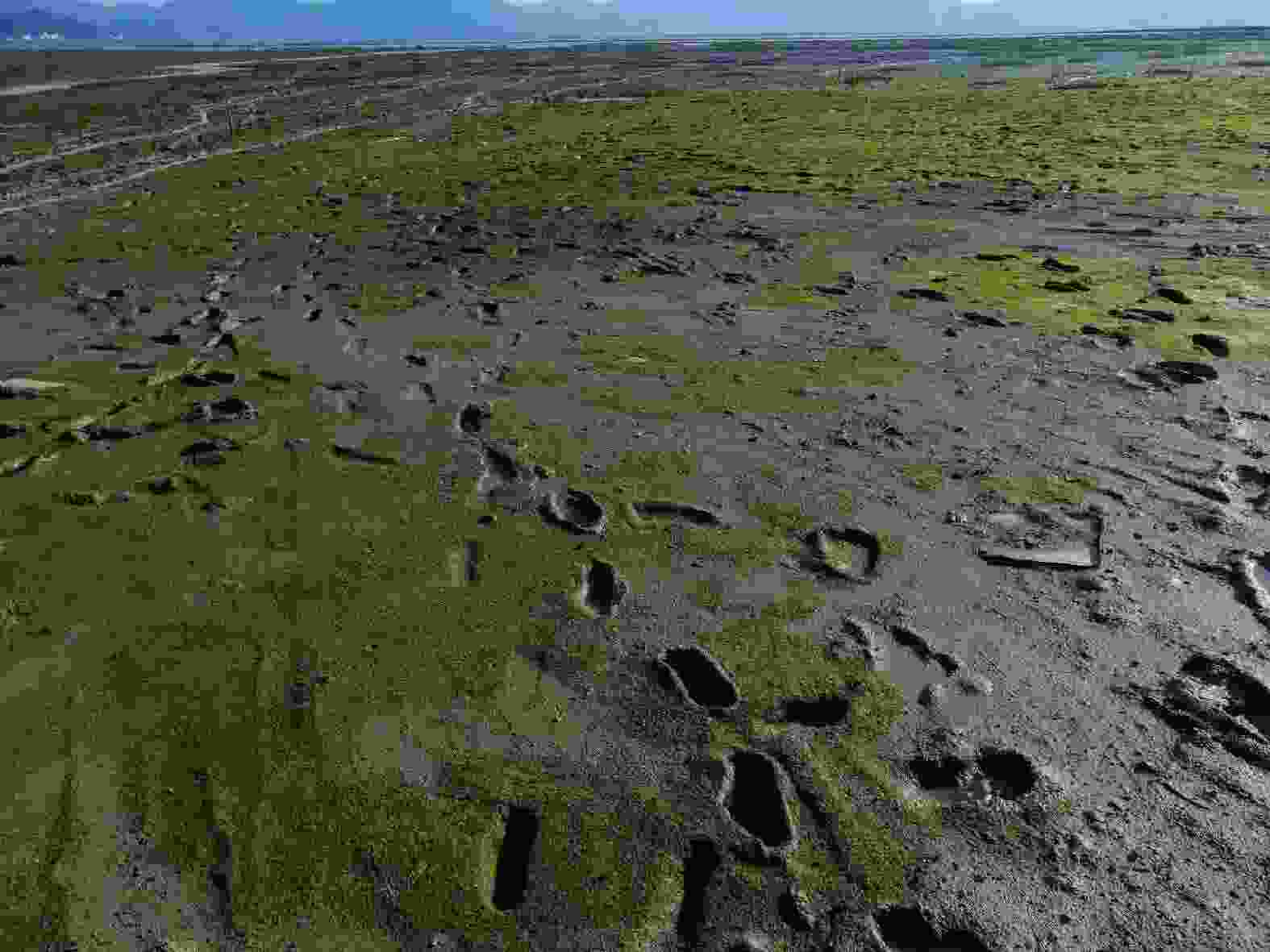
Abstract: Green tidal algal Enteromorpha species complete their life cycles by the isomorphic alternation of generations. The provenance of green tide caused by them in the western Yellow Sea has been disputed. The cell reproduction derived from adult thallus was observed on E. clathrata collected from Shantou City, Guangdong Province in this study. Subsequently, it further found that E. proliferia collected from Qingdao City, Shandong Province and Qinhuangdao City, Hebei Province, produced reproductive cells by somatic cells of its early infantile thallus or branch. The latter is functionally similar to that the seedlings of red alga Porphyra yezoensis produce the monospores, and could exquisitely explain the ephemeral or opportunistic trait and environmental adaptation ability of Enteromorpha species. Changes in growth conditions may induce the two types of cell reproduction. They contribute to the bloom, and can effectively reveal the seasonally occurring large-scale and on-year and off-year phenomenon. The latter may have played a decisive role in its formation. This paper analyses the legal status of the species name, the type of generation during bloom, ephemeral traits, the role of microscopic propagule, the area of origin, on-year and off-year phenomenon, early warning and prevention and control of the species, and so on. On this basis, further study on the influence of environmental factors on cell reproduction of early infantile thalli or branches will achieve a positive effect for early warning and prevention and control of the green tidal algal bloom.
-
Key words:
- green tidal algae /
- Yellow Sea /
- opportunistic trait /
- on-year and off-year /
- early infantile /
- alternation of generations /
- prediction on the occurrence process
1 1Ding Lanping, International Symposium of Advanced Research on Green Tides, May 09–11, 2014, Shanghai, China.
-
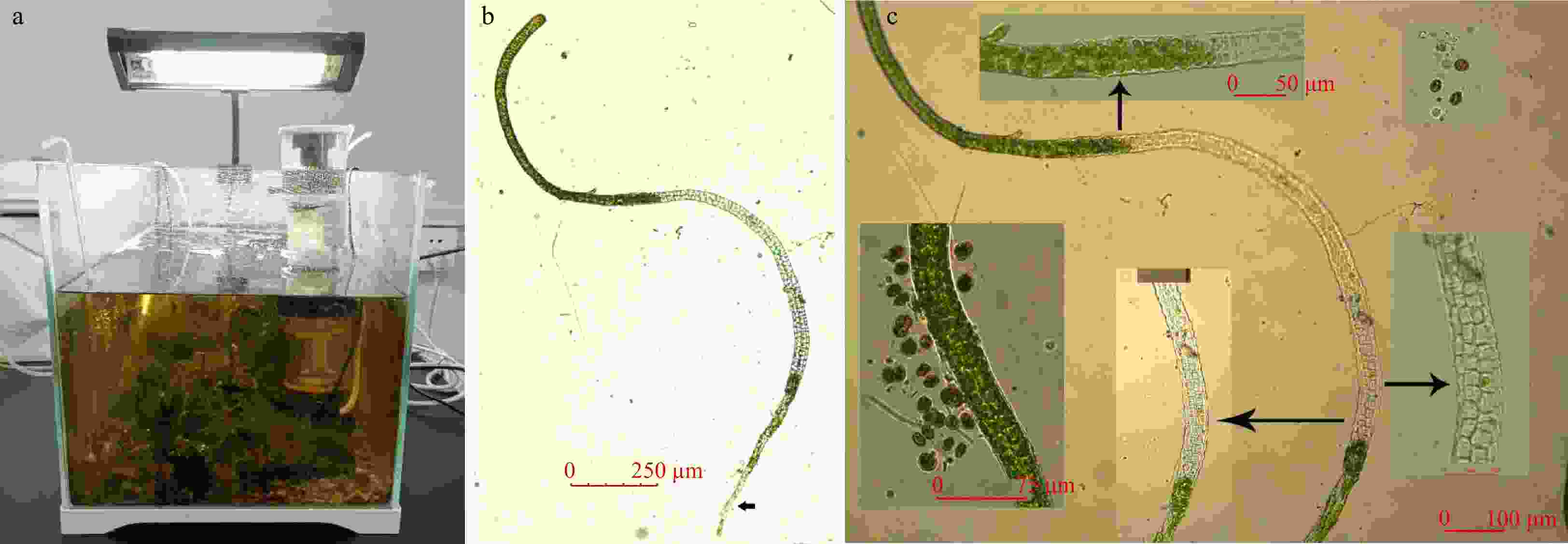
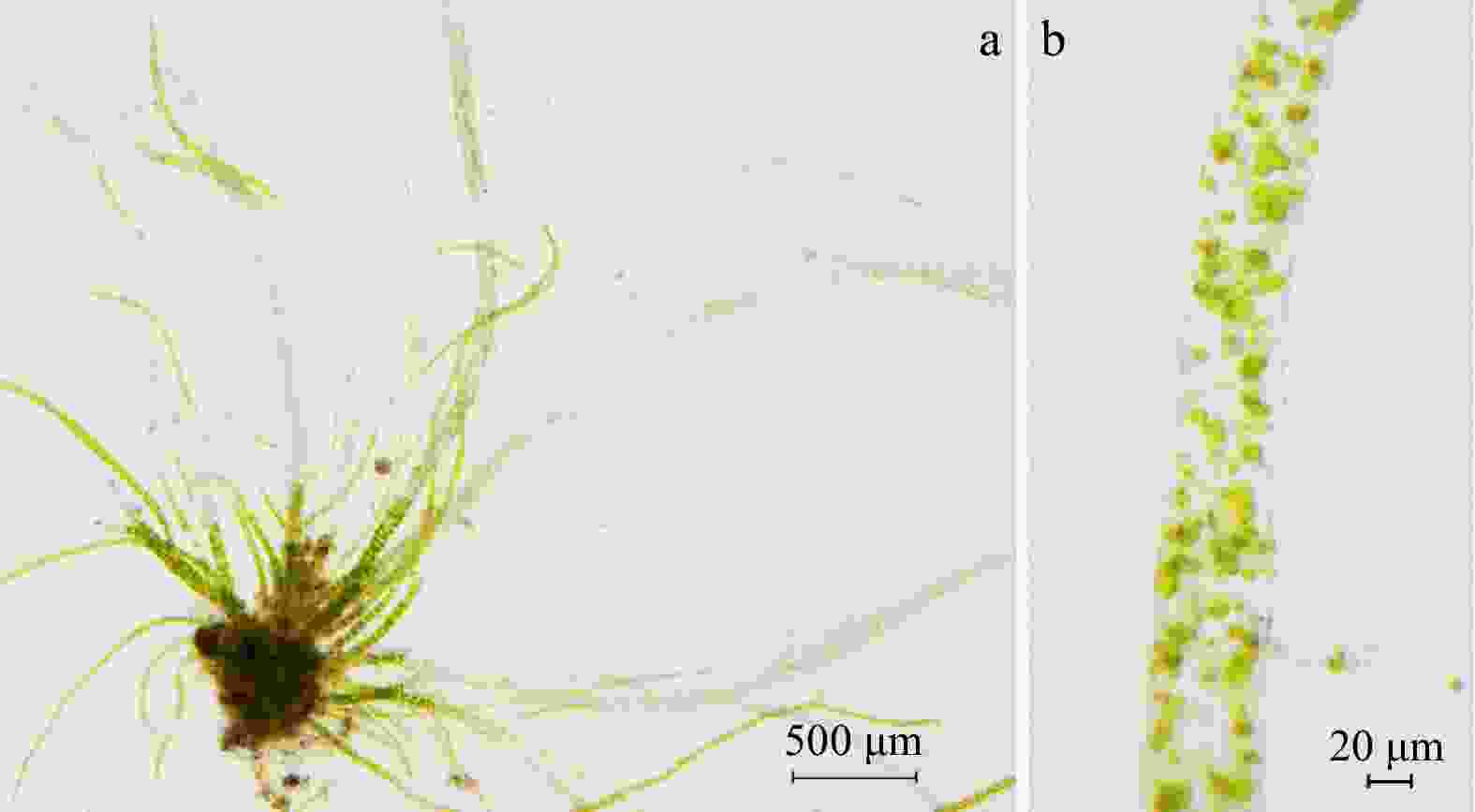
Figure 3. Cell reproduction of infantile Enteromorpha prolifera under room temperature. a. The indoor culture tank of infantile E. prolifera. b. The seedlings of E. prolifera (the thallus, short arrow shows the basal rhizoid). c. The part of the seedling unformed reproductive cells, and the reproductive cells formed near the base of the seedlings and remnants of cell walls after released.
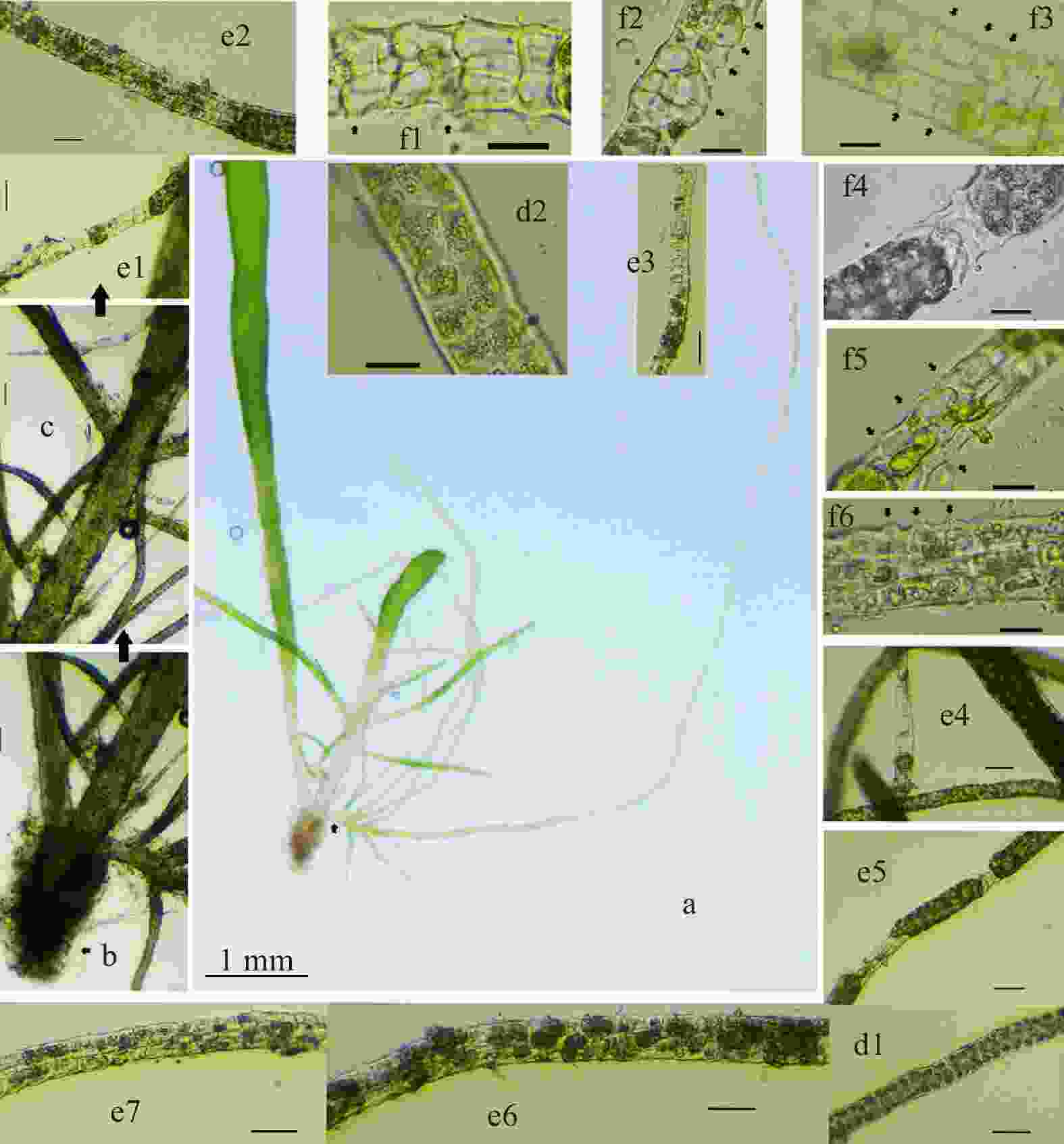
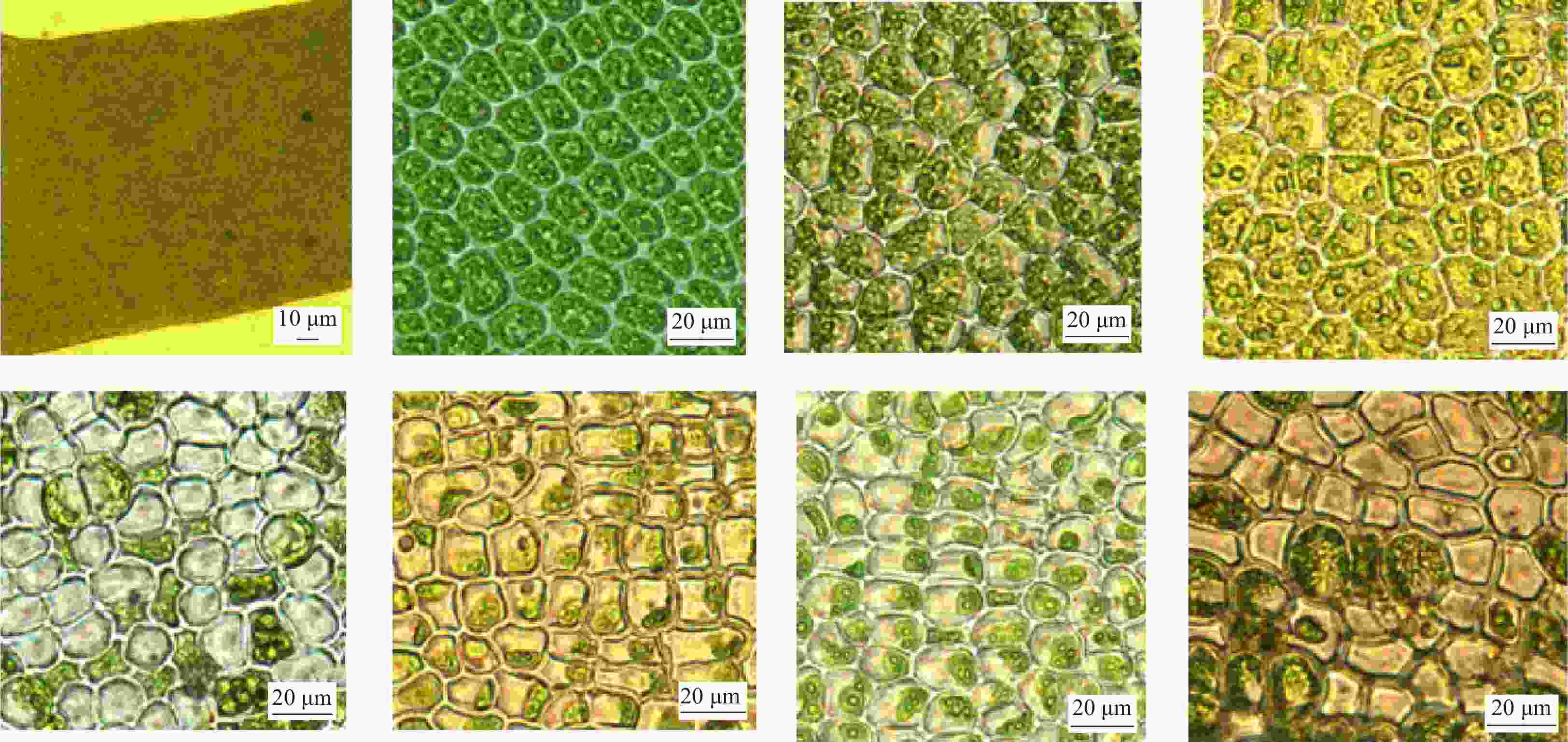
Figure 4. Adolescent Enteromorpha prolifera with reproductive cells formed and released at 22℃. a. Adolescent thalli (short arrow show the formation and release of reproductive cells at first-order branches); b. Base of the adolescent thalli (short arrows show the holdfast);c. Near the base of the adolescent thalli; d1–2. Branch cells of the adolescent thalli (d2 shows magnification image); e1–7. Formation of branches and their type and morphology released reproductive cells; f1–6. Reproductive cells released by the branched of adolescent thalli (magnification image, short arrows showed the ostiole releasing the reproductive cells) (scale bar: a. 1 mm; b. 100 μm; c. 100 μm; d1. 50 μm; d2. 20 μm; e1–7. 50 μm; f1–6. 20 μm) .
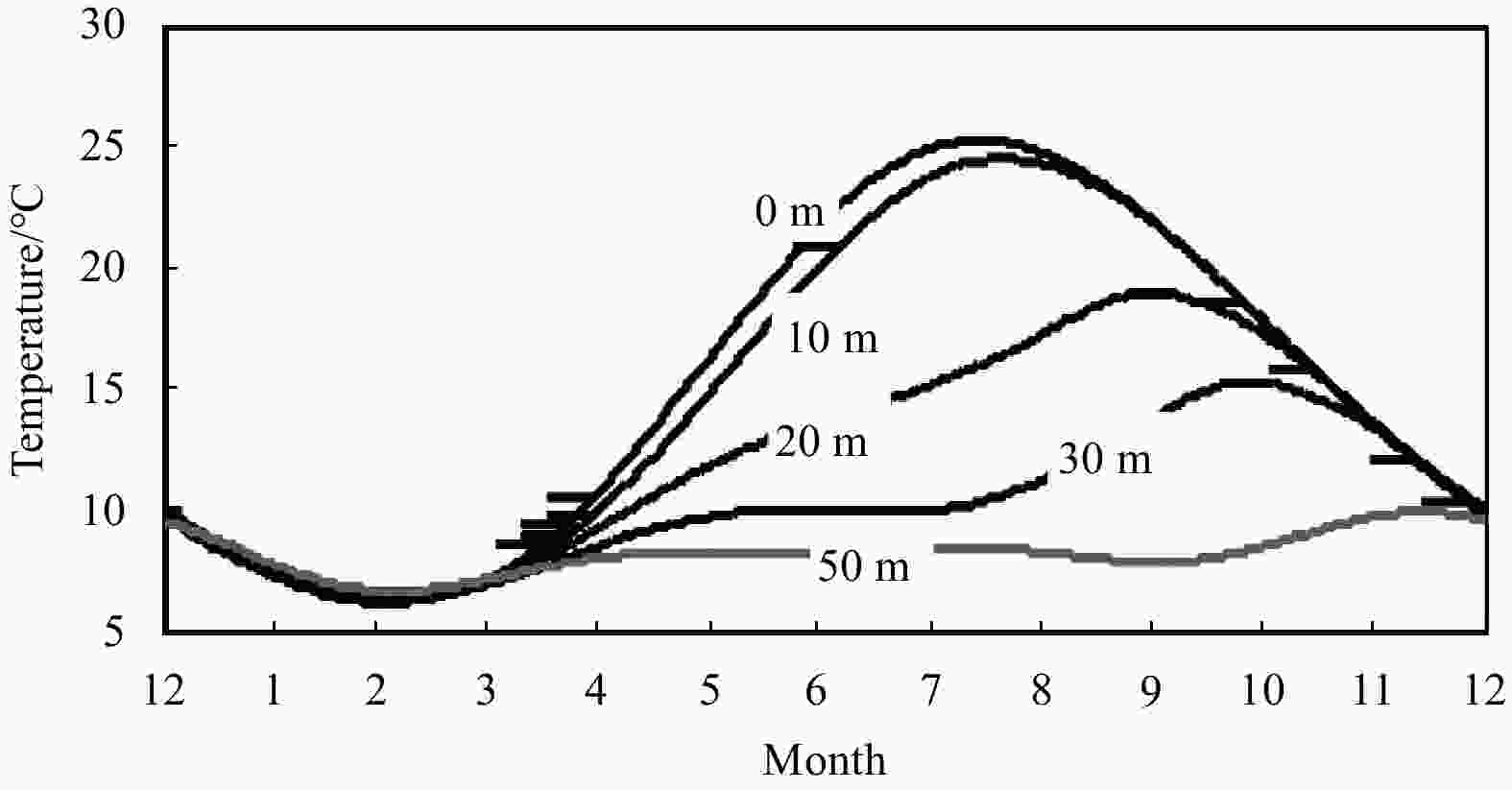
Figure 6. Seasonal variation of water temperature in the western part of the South Yellow Sea (Hu, 2013).
-
Clayton M N. 1992. Propagules of marine macroalgae: structure and development. British Phycological Journal, 27(3): 219–232. doi: 10.1080/00071619200650231 Cui Jianjun, Zhang Jianheng, Huo Yuanzi, et al. 2015. Adaptability of free-floating green tide algae in the Yellow Sea to variable temperature and light intensity. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101(2): 660–666. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.033 Deng Yunyan, Tang Xiaorong, Huang Bingxin, et al. 2011. The temperature character of marine green alga, Chaetomorpha valida, with analysis of its diffusion potential in marine algal flora of China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 42(3): 404–408 Ding Lanping. 2013. Flora Algarum Marinarum Sinicarum: Tomus IV Chlorophyta: No. I Ulotrichales, Chaetophorales, Phaeophilales, Ulvales, Prasiolales, Cladophorales, Acrosiphoniales (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press Ding Lanping. 2022. Species diversity of genus Entermorpha in coastal China with the legitimacy evaluation on the scientific name of E. prolifera as the main origin ones of green tides in the Yellow Sea (in Chinese). Life World, (3): 30–33 Ding Lanping, Fei Xiugeng, Lu Qinqin, et al. 2009. The Possibility analysis of habitats, origin and reappearance of bloom green alga (Enteromorpha prolifera) on inshore of western Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27(3): 421–424. doi: 10.1007/s00343-009-9277-x Ding Lanping, Luan Rixiao. 2009. The taxonomy, habit, and distribution of a green alga Enteromorpha prolifera (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 40(1): 68–71 Ding Lanping, Teng Linhong, Lu Qinqin, et al. 2014. The morphological comparison, variation and molecular analysis between two green tidal algae Enteromorpha prolifera and E. clathrata from China. Algological Studies, 145–146: 27–38 Fang Song, Wang Zongling, Li Yan, et al. 2012. The dynamics of micro-propagules before the green tide (Ulva prolifera) outbreak in the Southern Huanghai Sea and Changjiang (Yangtze) River Estuary area. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 34(4): 147–154 Feng Zihui, Meng Yang, Lu Wei, et al. 2012. Studies on photosynthesis carbon fixation and ocean acidification prevention in Ulva prolifera I. Rate of photosynthesis carbon fixation and seawater pH increase. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 34(2): 162–168 Gao Shan, Chen Xiaoyuan, Yi Qianqian, et al. 2010. A strategy for the proliferation of Ulva prolifera, main causative species of green tides, with formation of sporangia by fragmentation. PLoS ONE, 5(1): e8571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008571 Gordon R, Brawley S H. 2004. Effects of water motion on propagule release from algae with complex life histories. Marine Biology, 145(1): 21–29 Han Hongbin, Li Yan, Ma Xiaojun, et al. 2022. Factors influencing the spatial and temporal distributions of green algae micro-propagules in the coastal waters of Jinmenghaiwan, Qinhuangdao, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 175: 113328. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113328 Han Hongbin, Song Wei, Wang Zongling, et al. 2019. Distribution of green algae micro-propagules and their function in the formation of the green tides in the coast of Qinhuangdao, the Bohai Sea, China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 38(8): 72–77. doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1278-1 Han Hongbin, Wei Zhangliang, Huo Yuanzi, et al. 2015. Effects of temperature and light intensity on the release and germination of Ulva prolifera spores/gametes. Marine Fisheries (in Chinese), 37(6): 517–524 Hayden H S, Blomster J, Maggs C A, et al. 2003. Linnaeus was right all along: Ulva and Enteromorpha are not distinct genera. European Journal of Phycology, 38(3): 277–294. doi: 10.1080/1364253031000136321 He Peimin, Zhang Jianheng, Huo Yuanzi, et al. 2019. Green Tides of China (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press Hiraoka M, Dan A, Shimada S, et al. 2003. Different life histories of Enteromorpha prolifera (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) from four rivers on Shikoku Island, Japan. Phycologia, 42(3): 275–284. doi: 10.2216/i0031-8884-42-3-275.1 Hoffmann A J. 1987. The arrival of seaweed propagules at the shore: a review. Botanica Marina, 30(2): 151–166. doi: 10.1515/botm.1987.30.2.151 Hu Yingying. 2013. Seasonal and interannual variations of the water temperature in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China Huang Zhiyuan, Zhong Zheke, Zhang Xiaoping, et al. 2021. Formation mechanism and regulation measures of on-year and off-year of Moso Bamboo forest: a review. World Forestry Research (in Chinese), 34(5): 20–25 Huo Yuanzi, Han Hongbin, Hua Liang, et al. 2016. Tracing the origin of green macroalgal blooms based on the large scale spatio-temporal distribution of Ulva microscopic propagules and settled mature Ulva vegetative thalli in coastal regions of the Yellow Sea, China. Harmful Algae, 59: 91–99. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2016.09.005 Jiang Hongxia, Ni Xue, Hu Baoyun, et al. 2015. Physiological characteristics of floating Enteromorpha prolifera in the Yellow Sea. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences (in Chinese), 43(2): 355–357 Kamermans P, Malta E, Verschuure J M, et al. 1998. Role of cold resistance and burial for winter survival and spring initiation of an Ulva spp. (Chlorophyta) bloom in a eutrophic lagoon (Veerse Meer Lagoon, The Netherlands). Marine Biology, 131(1): 45–51. doi: 10.1007/s002270050295 Li Xinshu, Xu Juntian, Yao Dongrui, et al. 2013. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on the growth, photosynthesis and pigments of Ulva prolifera. Journal of Fisheries of China (in Chinese), 37(8): 1206–1212. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38319 Lin Apeng, Wang Chao, Qiao Hongjin, et al. 2009. Study on the photosynthetic performances of Enteromorpha prolifera collected from the surface and bottom of the sea of Qingdao sea area. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(3): 399–404 Liu Feng, Pang Shaojun, Chopin T, et al. 2013. Understanding the recurrent large-scale green tide in the Yellow Sea: temporal and spatial correlations between multiple geographical, aquacultural and biological factors. Marine Environmental Research, 83: 38–47. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2012.10.007 Liu Feng, Pang Shaojun, Shan Tifeng, et al. 2010. A novel method to quantify the microscopic stages of Ulva species in seawater and its applications in forcasting green tides of the Yellow Sea. Chinese Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 55(6): 468–473 Liu Feng, Pang Shaojun, Zhao Xiaobo, et al. 2012. Quantitative, molecular and growth analyses of Ulva microscopic propagules in the coastal sediment of Jiangsu Province where green tides initially occurred. Marine Environmental Research, 74: 56–63. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.12.004 Liu Xiangqing, Wang Zongling, Li Yan, et al. 2015. Effects of temperature on the germination of green algal micro-propagules in the sediment. Advances in Marine Science (in Chinese), 33(2): 219–226 Lotze H K, Schramm W, Schories D, et al. 1999. Control of macroalgal blooms at early developmental stages: Pilayella littoralis versus Enteromorpha spp. Oecologia, 119(1): 46–54. doi: 10.1007/s004420050759 Ma Wenfei, Li Jingyu. 2022. Analysis of the underlying mechanisms of green tide with a perspective of algae ecophysiology. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 33(5): 1420–1428 Ma Jiahai, Zhang Liming, Ji Chuanli, et al. 1998. On the refrigerated nets of Porphyra yezoensis and quality analysis of produce. Journal of Fisheries of China (in Chinese), 22(S1): 65–71 Miao Xiaoxiang, Xiao Jie, Pang Min, et al. 2018. Effect of the large-scale green tide on the species succession of green macroalgal micro-propagules in the coastal waters of Qingdao, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 126: 549–556. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.09.060 Miao Xiaoxiang, Xiao Jie, Wang Zongling, et al. 2020. Study on the tempo-spatial distribution of green macroalgal micro-propagules along the coasts of Jiangsu and Shandong Provinces. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 42(2): 115–123 Santelices B, Hoffmann A J, Aedo D, et al. 1995. A bank of microscopic forms on disturbed boulders and stones in tide pools. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 129(1–3): 215–228 Shen Songdong. 2022. Brief introduction of micropropagule. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 53(1): 1–7 Song Wei, Peng Keqin, Xiao Jie, et al. 2015. Effects of temperature on the germination of green algae micro-propagules in coastal waters of the Subei Shoal, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 163: 63–68 Taiz L, Zeiger E, Møller I M, et al. 2015. Plant Physiology and Development. 6th ed. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates Togashi T, Cox P A. 2001. Tidal-linked synchrony of gamete release in the marine green alga, Monostroma angicava Kjellman. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 264(2): 117–131 Wang Hui. 2017. Photosynthetic changes and response towards signaling molecule nitric oxide during the sporulation of Ulva prolifera (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Wang Hui, Lin Apeng, Gu Wenhui, et al. 2016. The sporulation of the green alga Ulva prolifera is controlled by changes in photosynthetic electron transport chain. Scientific Reports, 6: 24923. doi: 10.1038/srep24923 Wang Xiaokun, Ma Jiahai, Ye Daocai, et al. 2007a. Preliminary study on the life history of Enteromorpha prolifera. Marine Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 26(5): 112–116 Wang Guangce, Wang Hui, Gao Shan, et al. 2020. Study on the biological mechanism of green tide. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 51(4): 789–808 Wang Xiangyu, Wu Haiyi. 2015. Nutrient uptaking and growth performance of Ulva prolifera. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences (in Chinese), 31(4): 243–246, 252 Wang Jianwei, Yan Binlun, Lin Apeng, et al. 2007b. Ecological factor research on the growth and induction of spores release in Enteromorpha prolifera (chlorophyta). Marine Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 26(2): 60–65 Worm B, Lotze H K, Sommer U. 2001. Algal propagule banks modify competition, consumer and resource control on Baltic rocky shores. Oecologia, 128(2): 281–293. doi: 10.1007/s004420100648 Wu Hailong, Gao Guang, Zhong Zhihai, et al. 2018. Physiological acclimation of the green tidal alga Ulva prolifera to a fast-changing environment. Marine Environmental Research, 137: 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2018.02.018 Xia Bin, Ma Shaosai, Cui Yi, et al. 2009. Distribution of temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, nutrients and their relationships with green tide in Enteromorpha prolifera outbreak area of the Yellow Sea. Progress in Fishery Sciences (in Chinese), 30(5): 94–101 Xie Yanqi. 2013. The bioecological mechanism on green tidal blooming of Enteromorpha species (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Shantou: Shantou University Yang Jing, Zhang Si, Liu Guimei. 2017. Variability analysis of the Green Tide based on satellite remote sensing monitoring data from 2011 to 2016 in the Yellow Sea. Marine Forecasts (in Chinese), 34(3): 56–61 Ye Naihao, Zhang Xiaowen, Mao Yuze, et al. 2008. Life history of Enteromorpha prolifera under laboratory conditions. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (in Chinese), 15(5): 853–859 Zhang Xiaowen, Wang Hongxia, Mao Yuze, et al. 2010. Somatic cells serve as a potential propagule bank of Enteromorpha prolifera forming a green tide in the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Applied Phycology, 22(2): 173–180. doi: 10.1007/s10811-009-9437-6 Zhang Xiaowen, Xu Dong, Mao Yuze, et al. 2011. Settlement of vegetative fragments of Ulva prolifera confirmed as an important seed source for succession of a large-scale green tide bloom. Limnology and Oceanography, 56(1): 233–242. doi: 10.4319/lo.2011.56.1.0233 Zhang Yao, Yan Jing, Huang Bingxin, et al. 2023. The epiphytic macroalgae on red alga Gelidium amansii from Qinhuangdao area, Bohai Sea in autumn based on thermostatic incubation experiments. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 54(2): 493–451 Zhao Xiaohui, Cui Jianjun, Zhang Jianheng, et al. 2019. Reproductive strategy of the floating alga Ulva prolifera in blooms in the Yellow Sea based on a combination of zoid and chromosome analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 146: 584–590. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.018 Zou Dinghui, Xia Jianrong. 2004. Studies progresses of sexual reproductive ecology in seaweeds. Acta Ecologica Sinica (in Chinese), 24(12): 2870–2877 -




 下载:
下载: