Study on strength properties and soil behaviour type classification of Huanghe River Delta silts based on variable rate piezocone penetration test
-
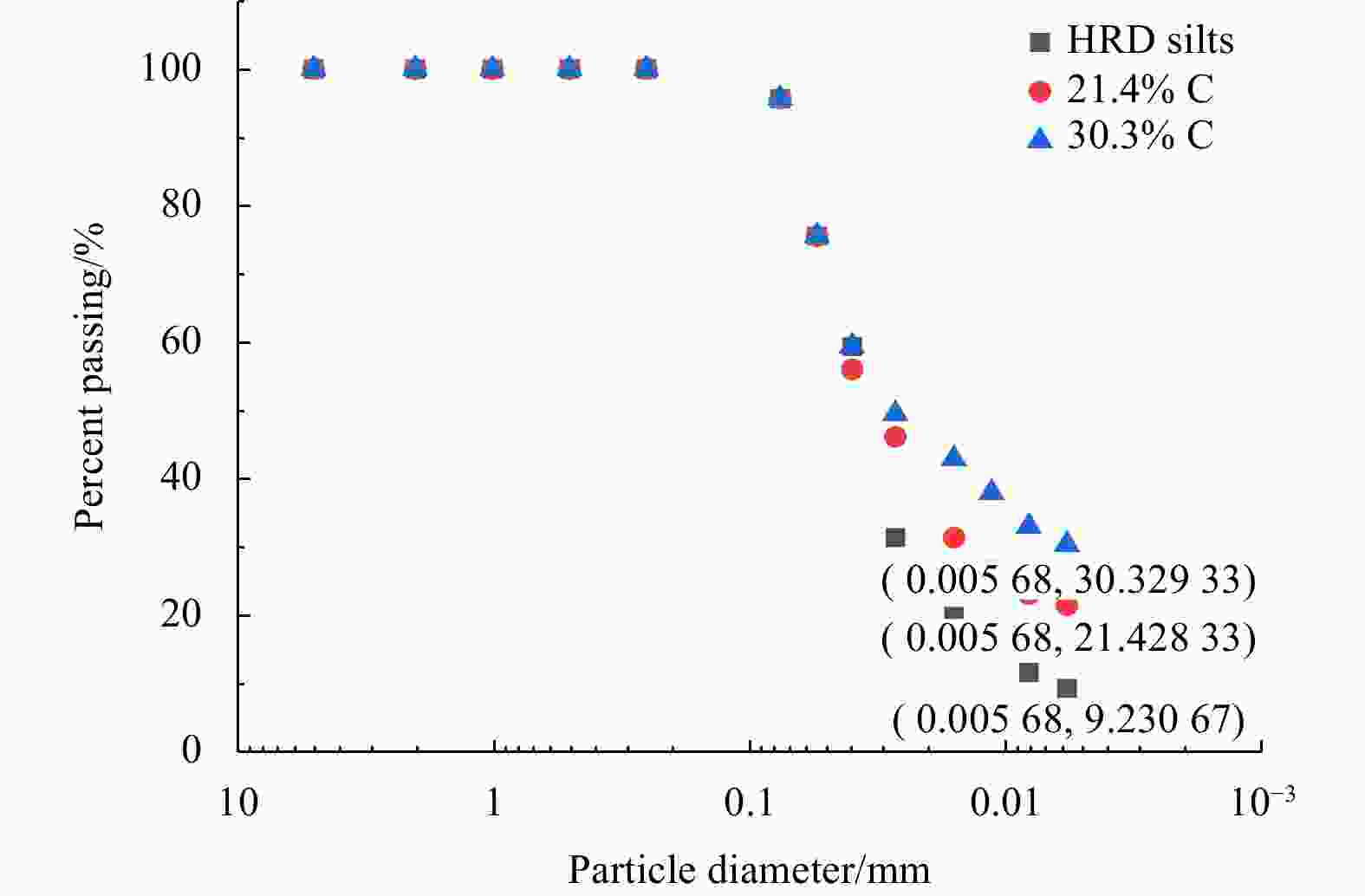
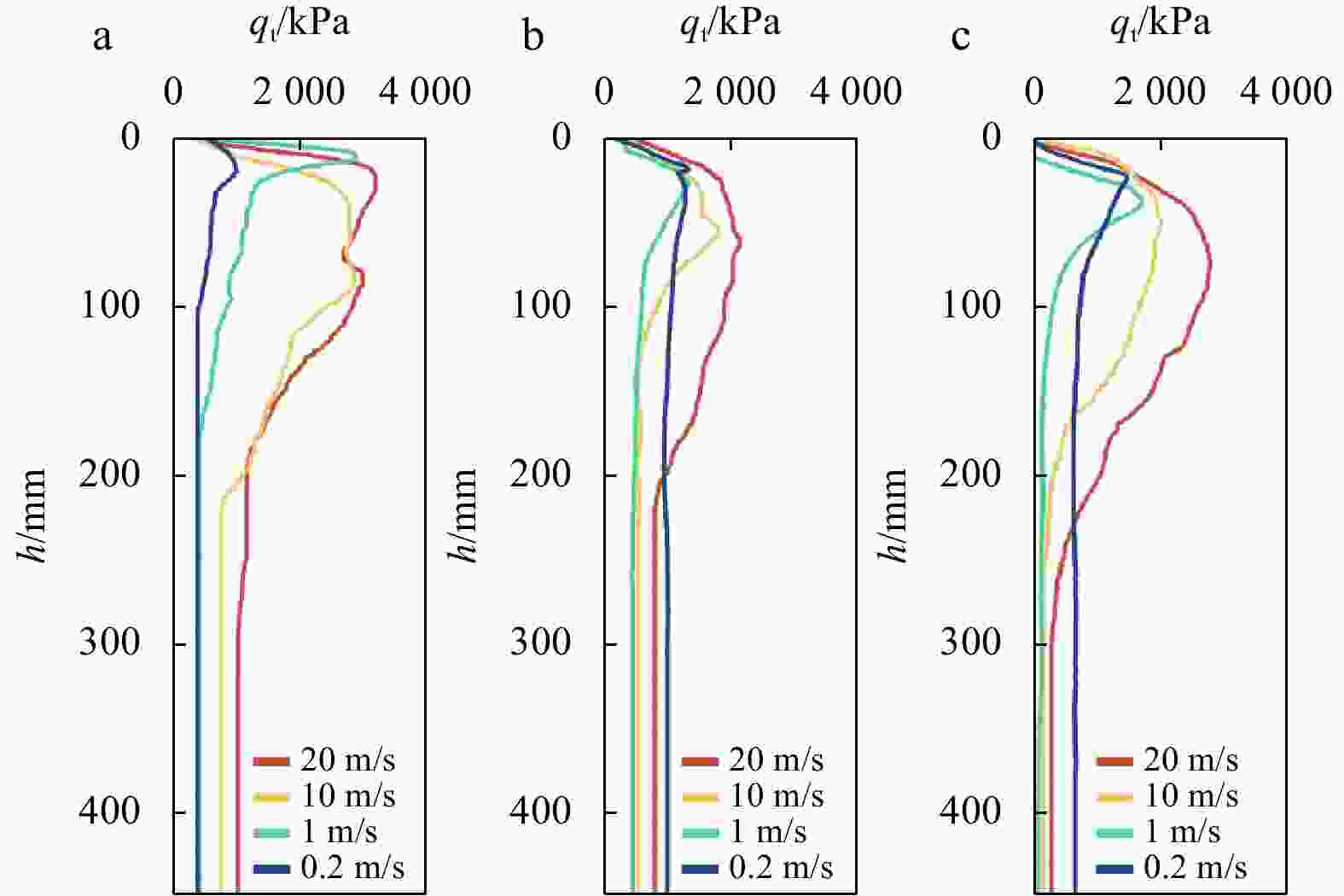
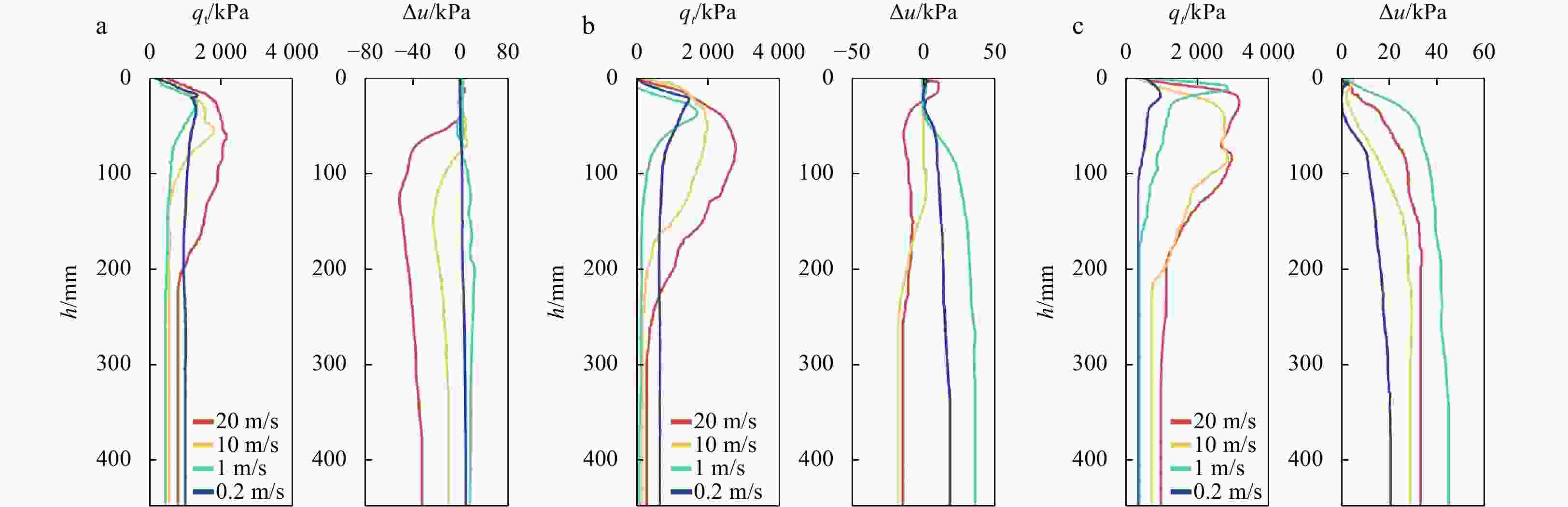
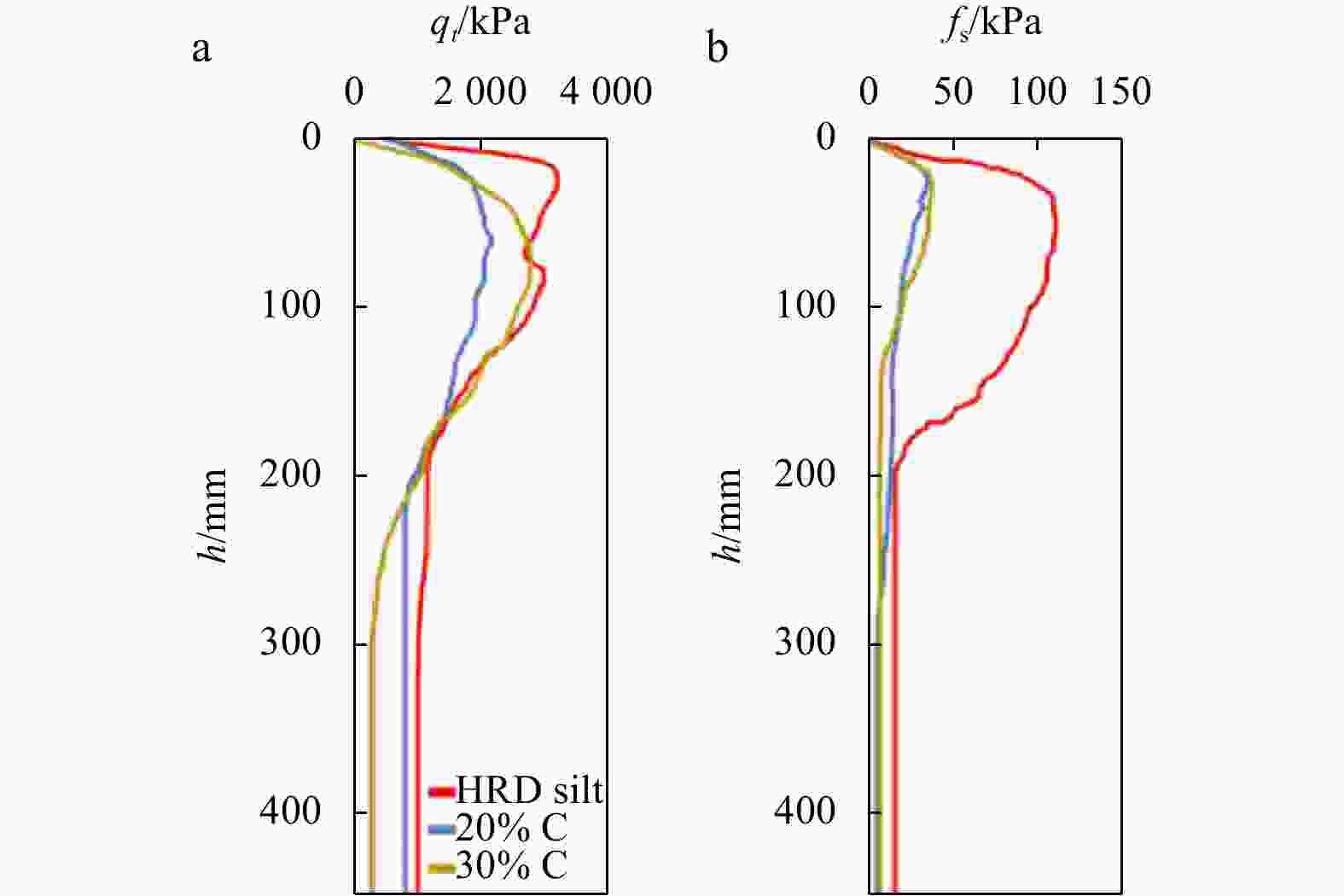
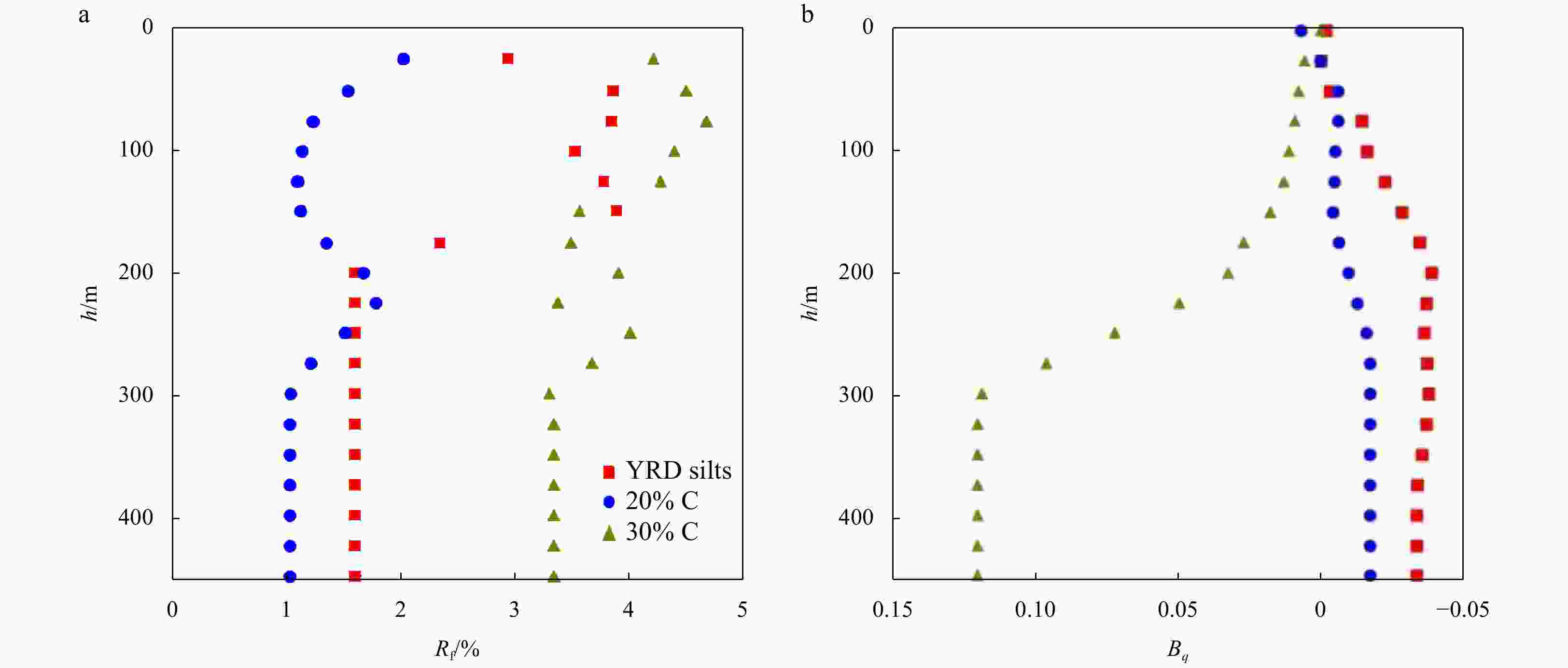
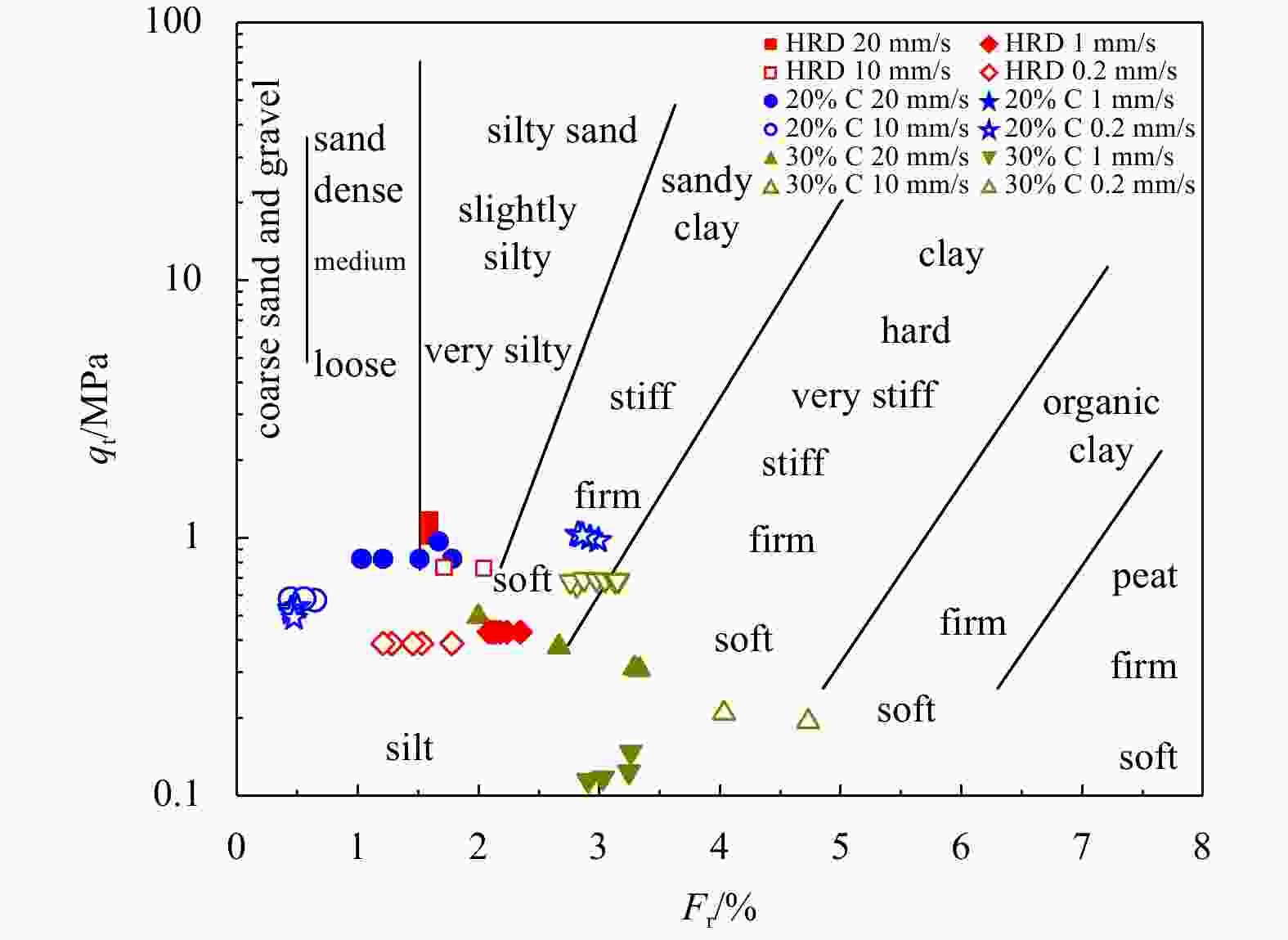
Abstract: Fine-grained silt is widely distributed in the Huanghe River Delta (HRD) in China, and the sedimentary structure is complex, meaning that the clay content in the silt is variable. The piezocone penetration test (CPTu) is the most widely approved in situ test method. It can be used to invert soil properties and interpret soil behavior. To analyse the strength properties of surface sediments in the HRD, this paper evaluated the friction angle and its inversion formula through the CPTu penetration test and monotonic simple shear test and other soil unit experiments. The evaluation showed that the empirical formula proposed by Kulhawy and Mayne had better prediction and inversion effect. The HRD silts with clay contents of 9.2%, 21.4% and 30.3% were selected as samples for the CPTu variable rate penetration test. The results show as follows. (1) The effects of the clay content on the tip resistance and the pore pressure of silt under different penetration rates were summarized. The tip resistance Qt is strongly dependent on the clay content of the silt, the
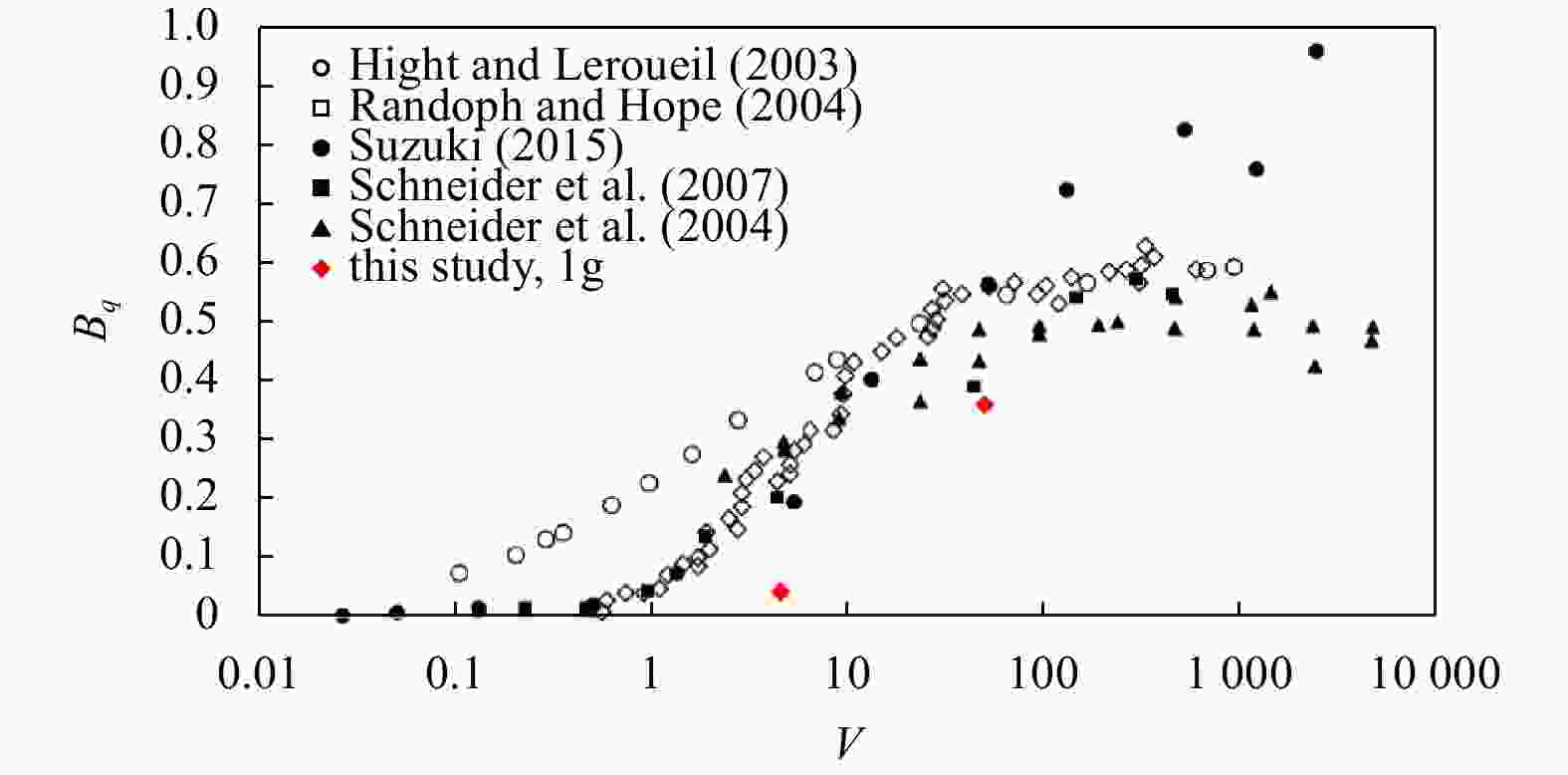
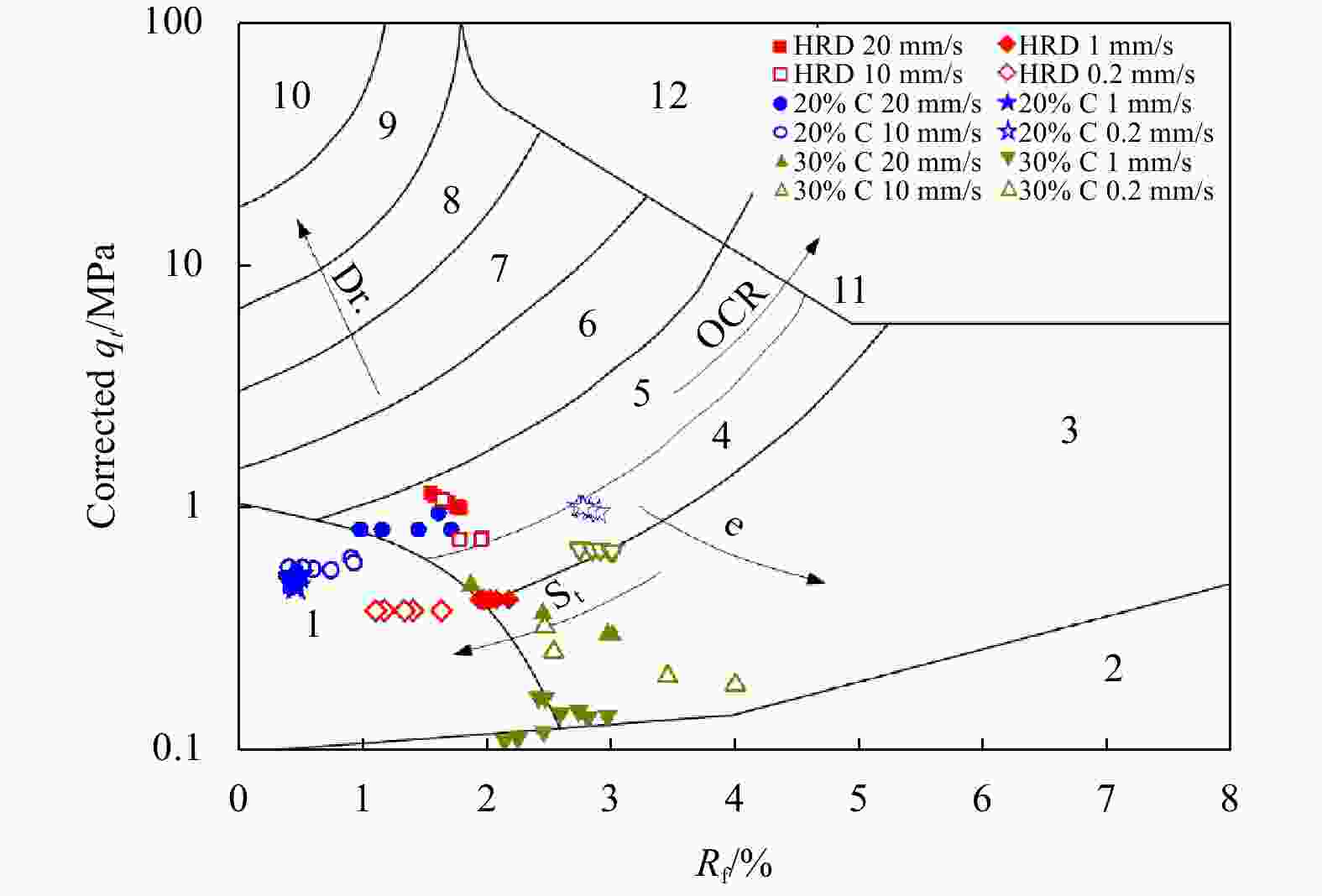
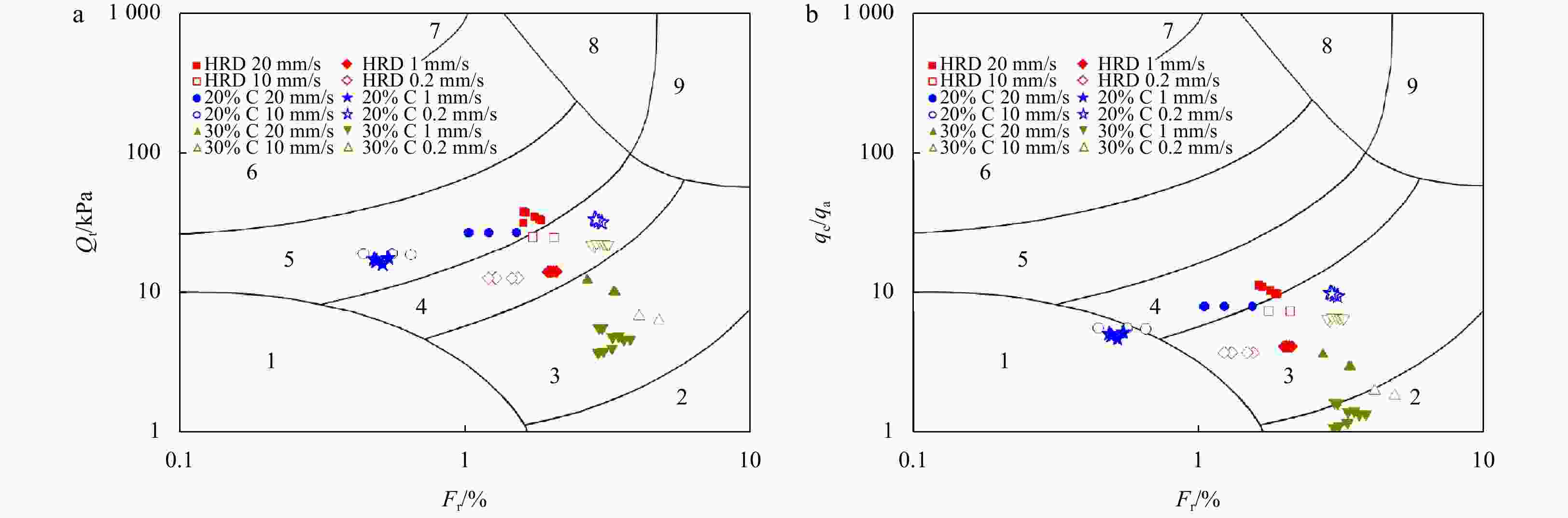
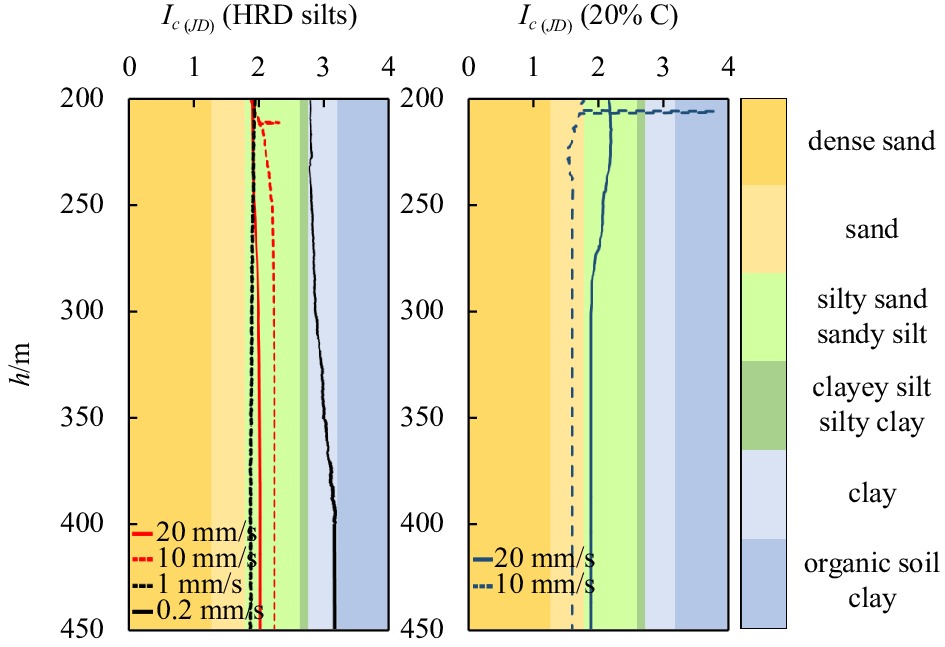
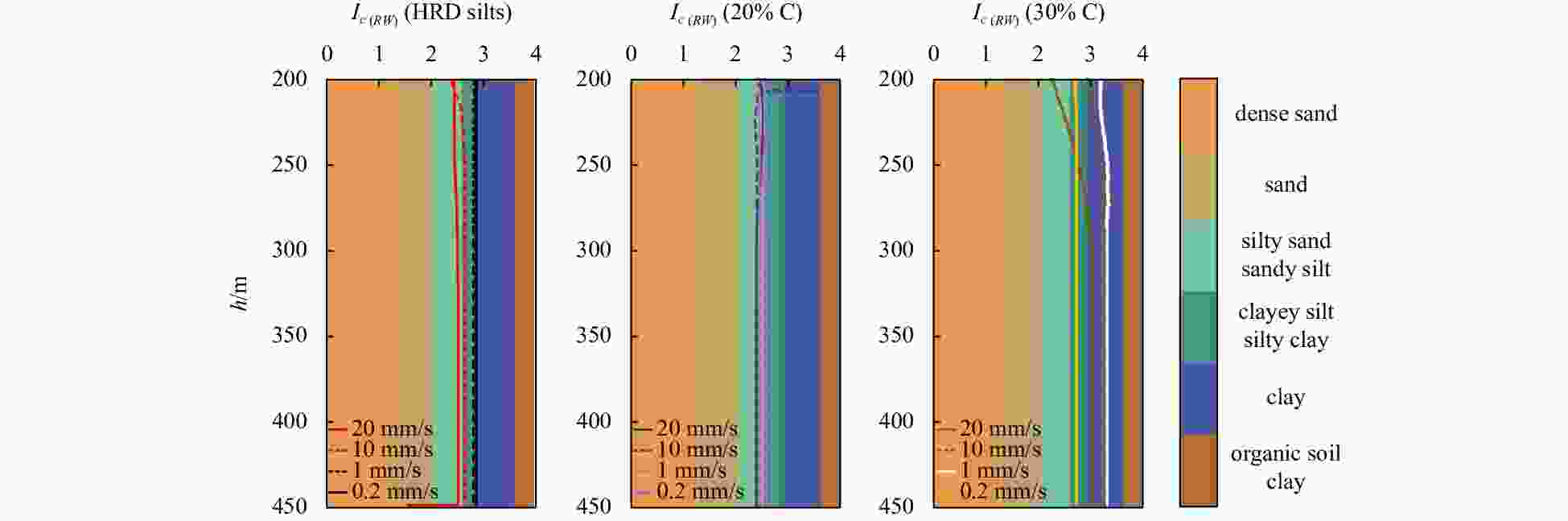
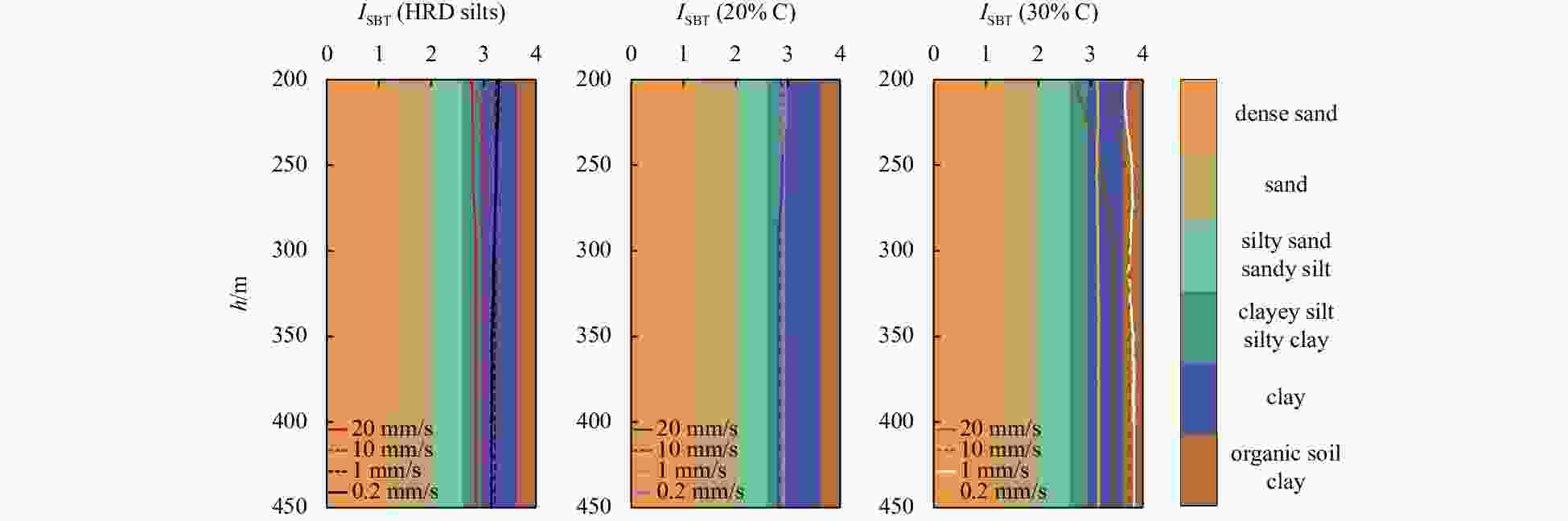
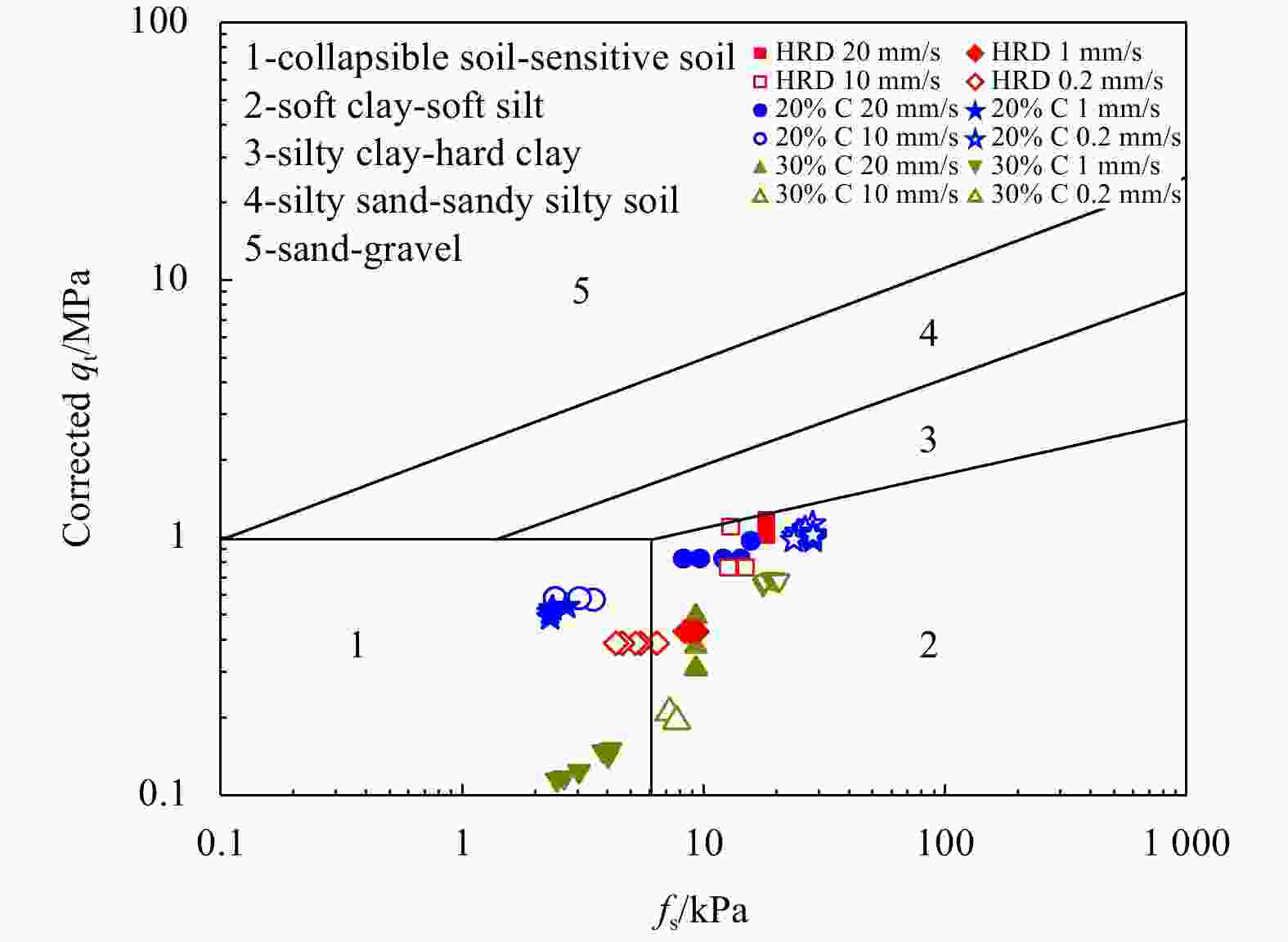
$ {B}_{q} $ value of the silt tends to 0 and is not significantly affected by the change of the CPTu penetration rate. (2) Five soil behavior type classification charts and three soil behavior type indexes based on CPTu data were evaluated. The results show that the soil behavior type classification chart based on soil behavior type index${I}_{{\rm{SBT}}}$ , the Robertson 2010 behavior type classification chart are more suitable for the silty soil in the HRD. -
Table 1. Soil properties of Huanghe River Delta silts
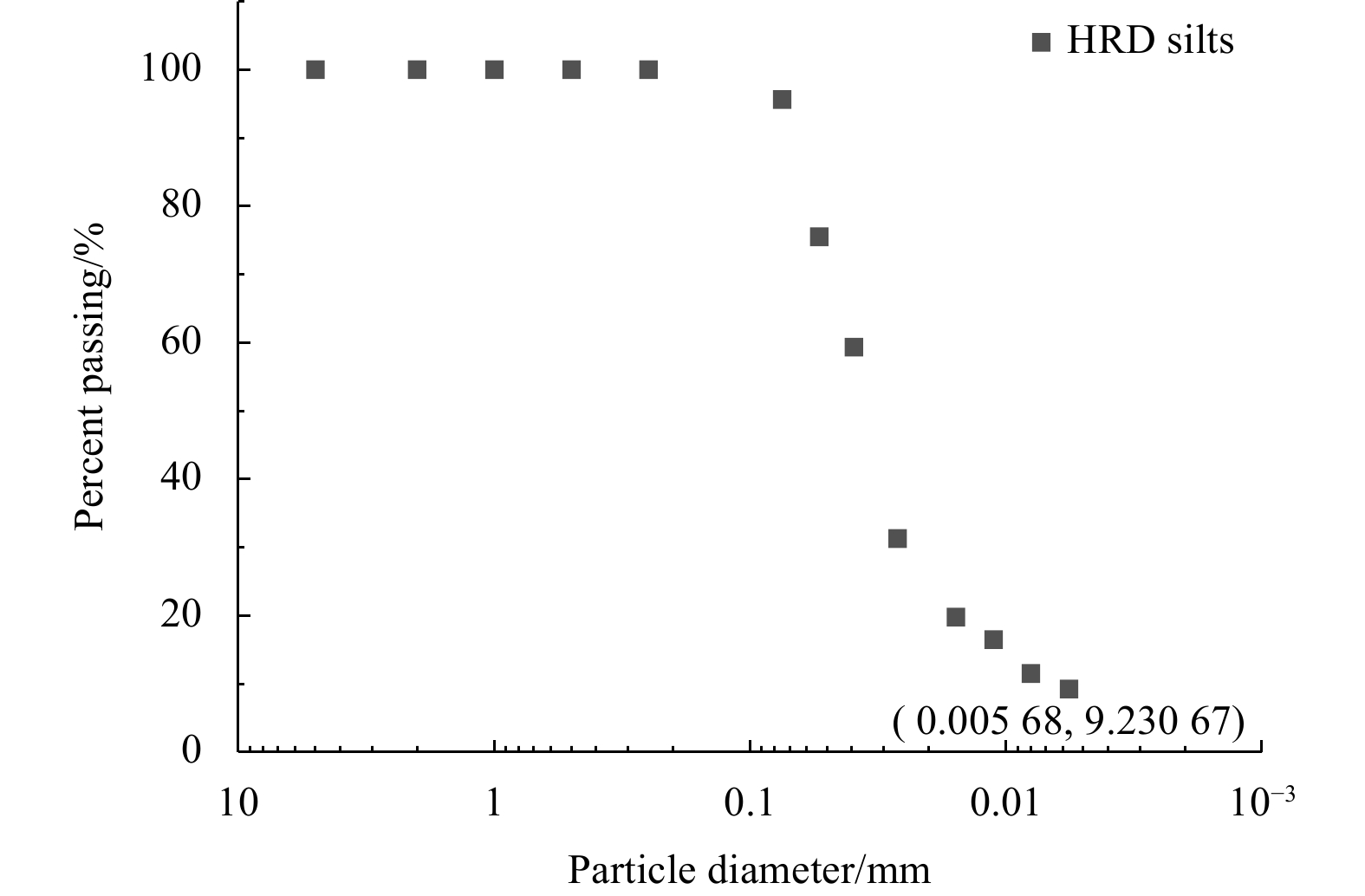
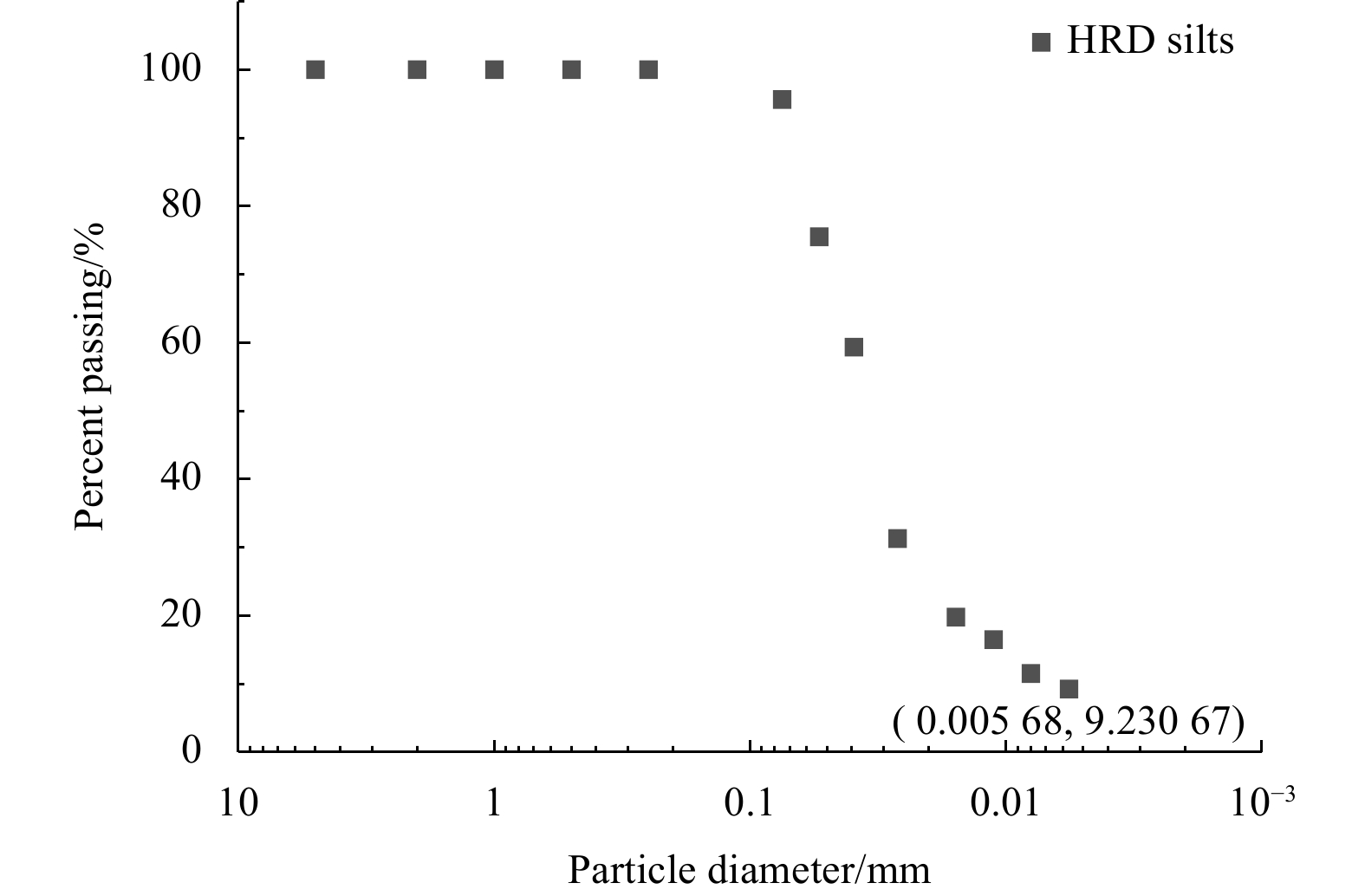
Soil type Specific gravity Water content/% emax emin $ {\rho }' $/(g·cm−3) Liquid limit/% Plastic limit/% Plasticity index Ip/% ML 2.70 25.4 1.45 0.45 1.25 29.6 21.6 9.8 Table 2. Consolidation coefficient (Cv) of Huanghe River Delta silts
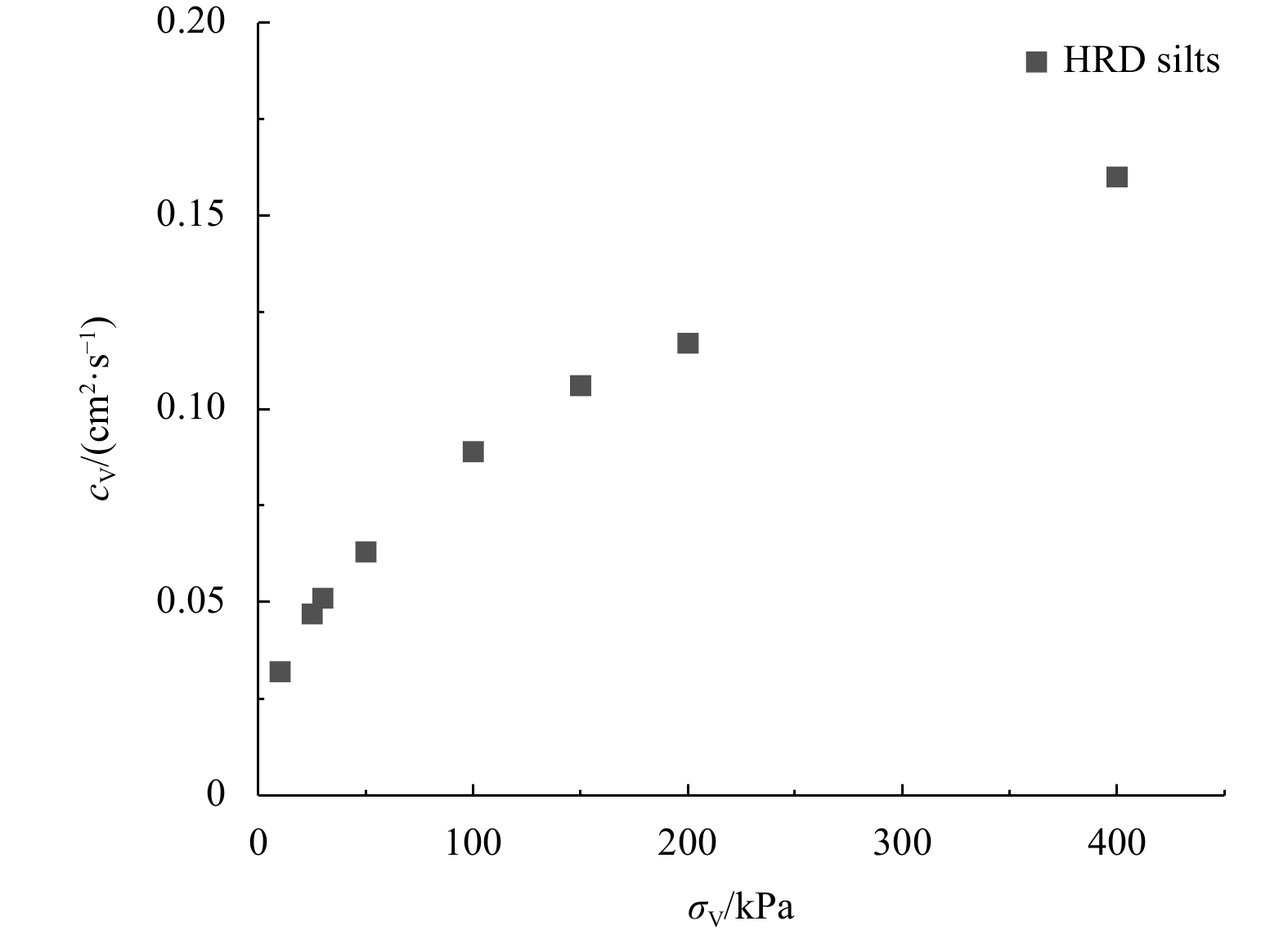
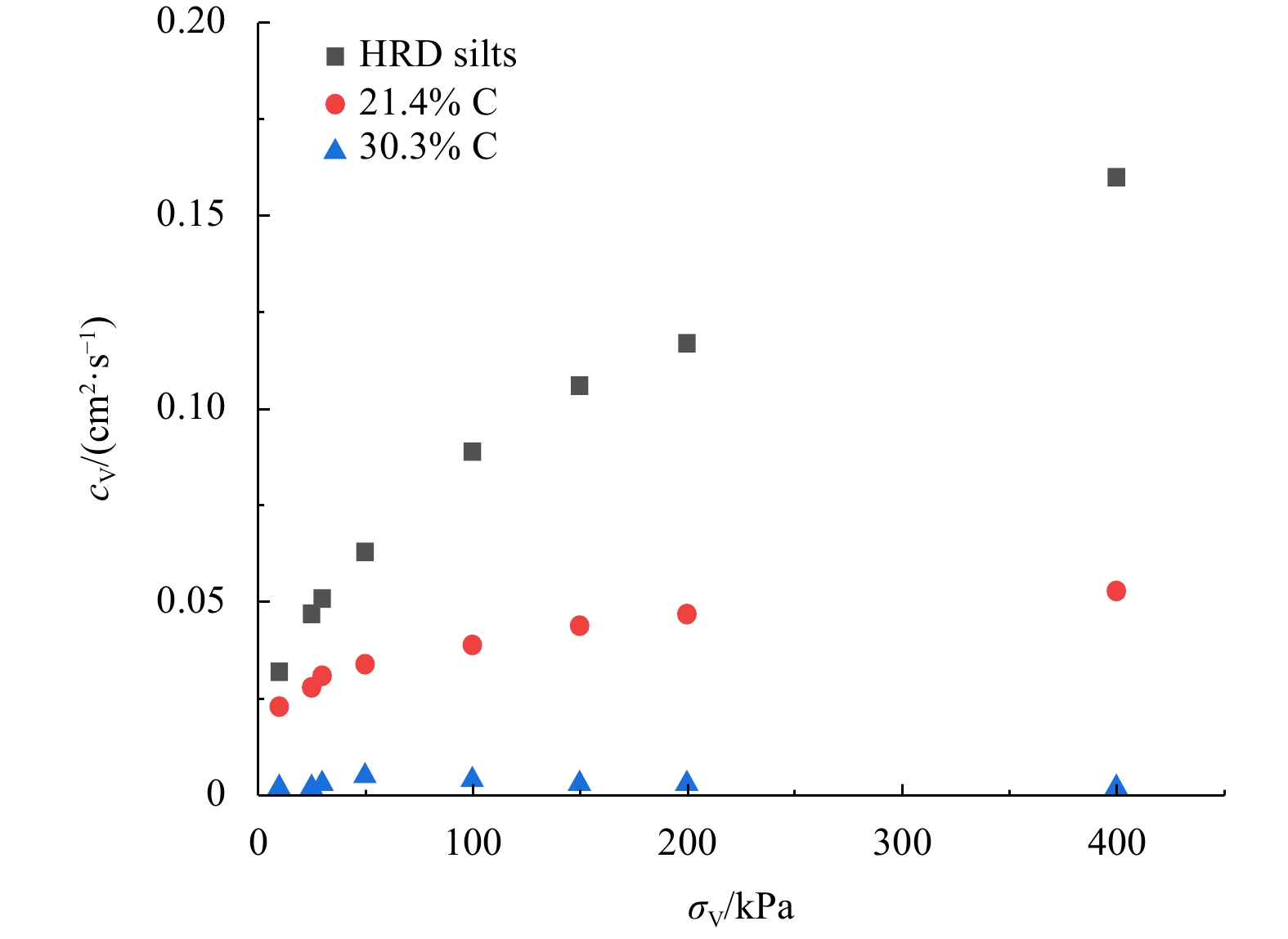
Vertical stress 30 kPa 50 kPa 100 kPa 150 kPa ${c}_{{\rm{v}}}$/(cm2·s−1) 0.051 0.063 0.089 0.106 Table 3. Friction angle obtained from monotonic shear test
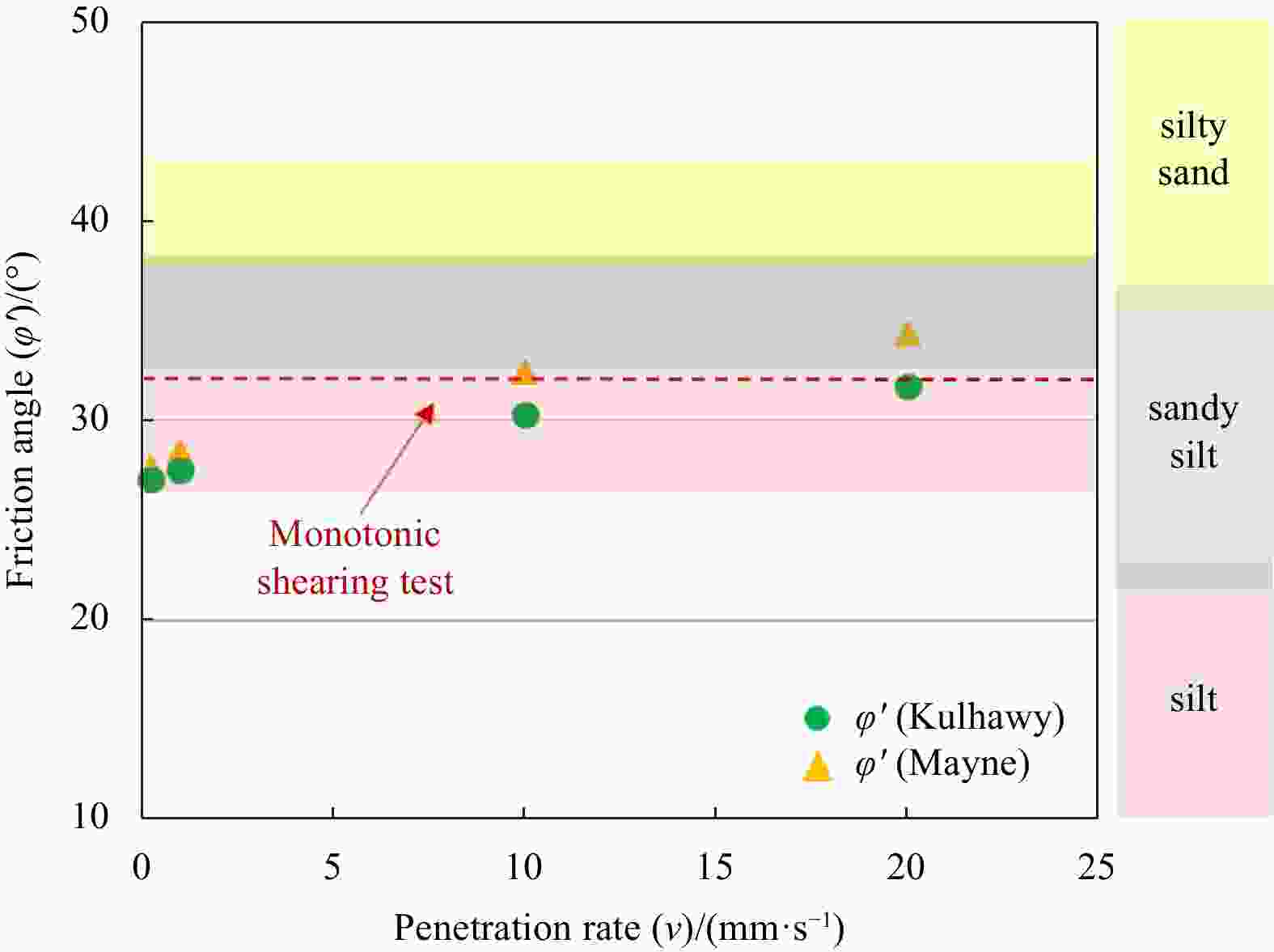
${\sigma }'_{ { {\rm{v} } }_{0} }$/kPa ${\varphi }{ {'} }$/(°) M 30 32.34 1.30 90 30.17 1.21 100 27.96 1.11 Table 4. Friction angle (
${\varphi '} $ ) derived from cone penetration testPenetration rate 20 mm/s 10 mm/s 1 mm/s 0.2 mm/s ${\varphi '}$ (Mayne) 34.34 32.43 28.41 27.65 ${\varphi '}$ (Kulhawy) 31.69 30.297 9 27.54 27.05 Table 5. Fiction angle corresponding to surface sediment types in the Huanghe River Delta
Soil types ${\varphi }' $/(°) Data source Normally consolidated
silty soil
26.5–38.3
Meng et al., 2008; Liu, 2014;
Lu and Li, 2003; Liu et al., 2006;
Chang, 2009; Cheng, 2007;
Liu et al., 2009; Wang et al., (2014Sandy silt 32.5–38.3 Chang, 2009; Jia et al., 2011 Silty sand 38.0–42.6 Table 6. Soil behaviour type classification
Region Soil type Region Soil type 1 sensitive fine-grained soil 7 silty sand-sandy silt 2 organic soil 8 sand-silty sand 3 clay 9 sand 4 silty clay-clay 10 gravel sand-sand 5 clayey silt-silty clay 11 very stiff fine-grained soil* 6 sandy silt-clayey silt 12 sand-clayey sand* Note: * refers to overconsolidated soil or cemented soil. Table 7. Soil behaviour type classification
Region Soil type Region Soil type 1
sensitive fine-grained
soil6
sand-silty san
2 organic soil, peats 7 gravelly sand-sand 3
clay-silty clay
8
very stiff sand-clayey
sand*4 clayey silt-silty clay 9 very stiff, fine grained* 5 silty sand-sandy silt Note: * refers to overconsolidated soil or cemented soil. -
Albatal A, Stark N, Castellanos B. 2020. Estimating in situ relative density and friction angle of nearshore sand from portable free-fall penetrometer tests. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 57(1): 17–31. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2018-0267 Begemann H K S. 1965. The friction jacket cone as an aid in determining the soil profile. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Montreal: Springer, 17−20 Brandon T L, Rose A T, Duncan J M. 2006. Drained and undrained strength interpretation for low-plasticity silts. Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering, 132(2): 250–257 Brouwer H. 2007. In Situ Soil Testing. East Sussex: Lankelma, 144 Cai Guojun, Liu Songyu, Puppala A J. 2011. Comparison of CPT charts for soil classification using PCPT data: example from clay deposits in Jiangsu Province, China. Engineering Geology, 121(1−2): 89–96. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.04.016 Chang Fangqiang. 2009. Study on mechanism of wave-induced submarine landslide at the Yellow River Estuary, China (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China Cheng Chao. 2007. Research on liquefaction evaluation criteria for silty soil in Yellow River Delta (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China Cheng Guodong, Xue Chunting. 1997. Sedimentary Geology of the Yellow River Delta (in Chinese). Beijing: Geological Publishing House Douglas B J, Olsen R S. 1981. Soil classification using electric cone penetrometer. In: Proceedings of Conference on Cone Penetration Testing and Experience. St. Louis: ASCE, 209–227 Eslami A, Fellenius B H. 1997. Pile capacity by direct CPT and CPTu methods applied to 102 case histories. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 34(6): 886–904. doi: 10.1139/t97-056 Feng Xiuli, Ye Yincan, Ma Yanxia, et al. 2002. Silt pore pressure response and dynamic strength under dynamic loading. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao (in Chinese), 32(3): 429–433 Finke K A, Mayne P W, Klopp R A. 2001. Piezocone penetration testing in Atlantic Piedmont residuum. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 127(1): 48–54. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2001)127:1(48) Geiser F, Laloui L, Vulliet L. 2006. Elasto-plasticity of unsaturated soils: laboratory test results on a remoulded silt. Soils and Foundations, 46(5): 545–556. doi: 10.3208/sandf.46.545 Holmsgaard R, Ibsen L B, Nielsen B N. 2016. Interpretation of seismic cone penetration testing in silty soil. Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 21(15): 4759–4779 Jefferies M G, Davies M P. 1991. Soil classification by the cone penetration test: Discussion. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 28(1): 173–176. doi: 10.1139/t91-023 Jefferies M G, Davies M P. 1993. Use of CPTU to estimate equivalent SPT N60. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 16(4): 458–468. doi: 10.1520/GTJ10286J Jia Yonggang, Shan Hongxian, Yang Xiujuan, et al. 2011. Sediment Dynamics and Geologic Hazards in the Estuary of Yellow River, China (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press Jones G A, Rust E. 1982. Piezometer penetration testing CUPT. In: 2nd European Symposium on Penetration Testing. Amsterdam: CRC Press, 607–613 Kulhawy F H, Mayne P W. 1990. Manual on estimating soil properties for foundation design. Palo Alto, CA: Electric Power Research Institute Librić L, Jurić-Kaćunić D, Kovačević M S. 2017. Application of Cone Penetration Test (Cpt) Results for Soil Classification. Građevinar, 69(1): 11–20 Liu Jie. 2014. Analysis of consolidation settlement and its contribution to topographical change in the Modern Yellow River subaqueous delta (in Chinese)[dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China Liu Xiaoyu, Liu Huixin, Sun Yongfu, et al. 2012. Experimental study of pore water pressure development mode of silt with different clay content under dynamic load. Coastal Engineering (in Chinese), 31(1): 1–7 Liu Hongjun, Lü Wenfang, Yang Junjie, et al. 2009. Influence of initial dry density and clay content on steady state strength of silty soil in Yellow River Delta. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering (in Chinese), 31(8): 1287–1291 Liu Shengfa, Zhuang Zhenye, Lü Haiqing, et al. 2006. The strata and environmental evolution in the late quaternary in the Chengdao area and modern Yellow River Delt Coast. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology (in Chinese), 2006(4): 32–37 Long M. 2008. Design parameters from in situ tests in soft ground—recent developments. In: Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterization. London: CRC Press, 89–116 Lu Hongyou, Li Guangxue. 2003. The features of scouring and silting and the prediction of water depth in the Chengdao area of the Yellow River Delta in recent years. Journal of Chang’an University: Earth Science Edition (in Chinese), 25(1): 57–61 Lunne T, Christoffersen H P. 1983. Interpretation of cone penetrometer data for offshore sands. In: Proceedings of the Annual Offshore Technology Conference. Richardson, Texas: 181–192 Mayne P W. 2006. The Second James K. Mitchell Lecture Undisturbed sand strength from seismic cone tests. Geomechanics and Geoengineering, 1(4): 239–257. doi: 10.1080/17486020601035657 Meng Xiangmei, Jia Yonggang, Liu Xiaoli. 2008. Study on zoning and liquefaction induced by wave of Chengdao in Yellow River Delta. Journal of Engineering Geology (in Chinese), 16(S1): 44–53 Mitchell J K, Lunne T A. 1978. Cone resistance as measure of sand strength. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, 104(7): 995–1012. doi: 10.1061/AJGEB6.0000676 Qi Shanzhong, Liu Haili. 2017. Natural and anthropogenic hazards in the Yellow River Delta, China. Natural Hazards, 85(3): 1907–1911. doi: 10.1007/s11069-016-2638-9 Robertson P K. 1990. Soil classification using the cone penetration test. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 27(1): 151–158. doi: 10.1139/t90-014 Robertson P K. 2009. Interpretation of cone penetration tests—a unified approach. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 46(11): 1337–1355. doi: 10.1139/T09-065 Robertson P K. 2010. Soil behaviour type from the CPT: an update. In: 2nd International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing. Huntington Beach: Cone Penetration Testing Organizing Committee, 575–583 Robertson P K, Campanella R G. 1983. Interpretation of cone penetration tests. Part I: Sand. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 20(4): 719–733 Robertson P K, Campanella R G, Gillespie D. 1986. Seismic CPT to measure in situ shear wave velocity. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 112(8): 791–803. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1986)112:8(791) Robertson P K, Wride C E. 1998. Evaluating cyclic liquefaction potential using the cone penetration test. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 35(3): 442–459. doi: 10.1139/t98-017 Senneset K, Janbu N. 1985. Shear strength parameters obtained from static cone penetration tests. In: Strength Testing of Marine sediments: Laboratory and In-Situ Measurement. West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 41–54 Shahri A A, Malehmir A, Juhlin C. 2015. Soil classification analysis based on piezocone penetration test data—A case study from a quick-clay landslide site in southwestern Sweden. Engineering Geology, 189: 32–47. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.01.022 Schneider J A, Randolph M F, Mayne P W, et al. 2008. Analysis of factors influencing soil classification using normalized piezocone tip resistance and pore pressure parameters. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 134(11): 1569–1586. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:11(1569) Song Binghui, Sun Yongfu, Song Yupeng, et al. 2020. Post-liquefaction re-compaction effect on the cyclic behavior of natural marine silty soil in the Yellow River Delta. Ocean Engineering, 195: 106753. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106753 Suzuki Y. 2015. Investigation and interpretation of cone penetration rate effects [dissertation]. Crawley, WA, Australia: The University of Western Australia Tonni L, Gottardi G. 2011. Analysis and interpretation of piezocone data on the silty soils of the Venetian lagoon (Treporti test site). Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 48(4): 616–633. doi: 10.1139/t10-085 Wang Hu, Liu Hongjun. 2016. Evaluation of storm wave-induced silty seabed instability and geo-hazards: A case study in the Yellow River Delta. Applied Ocean Research, 58: 135–145. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2016.03.013 Wang Xiaohua, Liu Hongjun, Jia Yonggang. 2008. The research on the mineral characteristics of sediment and the responce to the hydrodynamic conditions of the tidal flat, at the northern Yellow River Delta. Marine Science (in Chinese), 32(2): 42–46 Wang Hu, Liu Hongjun, Zhang Minsheng, et al. 2014. Undrained shear strength behavior of ocean silt under low stress conditions and its application to analyzing submarine shallow landslides. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering (in Chinese), 33(4): 849–856 Wen Mingzheng, Wang Zhenhao, Zhang Bowen, et al. 2018. Survey on the distribution of fluid mud and disturbed strata on subaqueous Yellow River Delta. Journal of Engineering Geology (in Chinese), 26(S1): 677–683 Yang Zhongnian, Liu Xuesen, Su Xiuting, et al. 2022. CPT-Based evaluation of sediment characteristics and effective internal friction angle in the Yellow River Estuary. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 40(9): 1108–1118 Yang Zhongnian, Zhu Yongmao, Liu Tao, et al. 2019. Pumping effect of wave-induced pore pressure on the development of fluid mud layer. Ocean Engineering, 189: 106391. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106391 Zhang Yan, Feng Xiuli, Deng Shenggui, et al. 2022a. Pore pressure response and dissipation of piezocone test in shallow silty soil of Yellow River Delta. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(2): 225. doi: 10.3390/jmse10020225 Zhang Yan, Feng Xiuli, Ding Chenhao, et al. 2022b. Study of cone penetration rate effects in the Yellow River Delta silty soils with different clay contents and state parameters. Ocean Engineering, 250: 110982. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110982 Zhang Jiarui, Meng Qingsheng, Zhang Yan, et al. 2022c. Effect of penetration rates on the piezocone penetration test in the Yellow River Delta silt. Journal of Ocean University of China, 21(2): 361–374. doi: 10.1007/s11802-022-4934-1 -






 下载:
下载: